Difference between ASP and DSP
Key difference: ASP stands for analog signal processing. Analog signal processing is basically any signal processing that is done on analog signals by analog means. DSP, on the other hand, is digital signal processing. It is basically any signal processing that is done on a digital signal or information signal. It aims to modify or improve the signal.
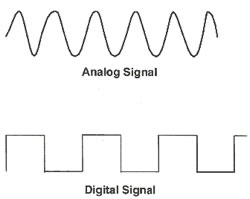
 Among other things, ASP also stands for analog signal processing. Analog signal processing is basically any signal processing that is done on analog signals by analog means. Analog is a linear transmission of signal, in which the amplitude varies. Analog is also mathematically represented as a set of continuous values.
Among other things, ASP also stands for analog signal processing. Analog signal processing is basically any signal processing that is done on analog signals by analog means. Analog is a linear transmission of signal, in which the amplitude varies. Analog is also mathematically represented as a set of continuous values.
Analog values are usually represented as voltage, electric current or electric charge around components in electronic devices. Some examples of analog signal processing include crossover filters in loudspeakers; bass, treble and volume on stereos; tint on televisions; capacitors; resistors; inductors; transistors; etc.
DSP, on the other hand, is digital signal processing. It is basically any signal processing that is done on a digital signal or information signal. It aims to modify or improve the signal. It is characterized by the representation of discrete units, such as discrete time, discrete frequency, or discrete domain signals. DSP includes subfields like communication signals processing, radar signal processing, sensor array processing, digital image processing, etc.
The main goal of DSP is to measure, filter and/or compress digital or analog signals. It does this by converting the signal from a real-world analog signal to a digital form. In order to convert the signal it uses a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). However, the required output signal is often another real-world analog signal. This is turn requires a digital-to-analog converter.
Digital signal processing algorithms run on various platforms, such as general purpose microprocessors and standard computers; specialized processors called digital signal processors (DSPs); purpose-built hardware such as application-specific integrated circuit (ASICs) and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs); Digital Signal Controllers; and stream processing for traditional DSP or graphics processing applications, such as image, video.
 Digital signal processing is more complex in nature than analog signal processing; however it is has many advantages over ASP, such as error detection, correction in transmission, and data compression. Transtutors.com lists several advantages that DSP has over ASP:
Digital signal processing is more complex in nature than analog signal processing; however it is has many advantages over ASP, such as error detection, correction in transmission, and data compression. Transtutors.com lists several advantages that DSP has over ASP:
- Digital signal processing operations can be changed by changing the program in digital programmable system, i.e., these is flexible systems.
- Better control of accuracy in digital systems compared to analog systems.
- Digital signals are easily stored on magnetic media such as magnetic tape without loss of quality of reproduction of signal.
- Digital signals can be processed off line, i.e., these are easily transported.
- Sophisticated signal processing algorithms can be implemented by DSP method.
- Digital circuits are less sensitive to tolerances of component values.
- Digital systems are independent of temperature, ageing and other external parameters.
- Digital circuits can be reproduced easily in large quantities at comparatively lower cost.
- Cost of processing per signal in DSP is reduced by time-sharing of given processor among a number of signals.
- Processor characteristics during processing, as in adaptive filters can be easily adjusted in digital implementation.
- Digital system can be cascaded without any loading problems.
Image Courtesy: tower.com, wrongplanet.net









Add new comment