Difference between Alpha Cell and Beta Cell
Key Difference: The alpha cell is responsible for synthesizing and secreting the peptide hormone glucagon, which elevates the glucose levels in the blood. The beta cell is an endocrine cell that is responsible for the production, storage and release of insulin.
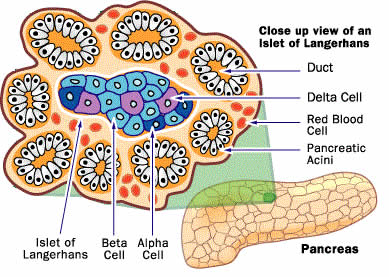 In order to understand alpha and beta cells in the body, we must first look at the region in which they are found. The alpha and the beta cells are found in islets of Langerhans, a region in the pancreas. The pancreas is a glandular organ, which means it is a gland that is responsible for producing various hormones inside the body. The pancreas is a part of the digestive system and is found in the abdomen. The pancreas is a dual-function gland, having features of both endocrine and exocrine glands.
In order to understand alpha and beta cells in the body, we must first look at the region in which they are found. The alpha and the beta cells are found in islets of Langerhans, a region in the pancreas. The pancreas is a glandular organ, which means it is a gland that is responsible for producing various hormones inside the body. The pancreas is a part of the digestive system and is found in the abdomen. The pancreas is a dual-function gland, having features of both endocrine and exocrine glands.
The islet of Langerhans are specific regions in the pancreas that contain the endocrine cells. This region was discovered by German pathological anatomist Paul Langerhans at the age of 22, in 1869. There are about 1 million islets that are distributed throughout the pancreas of a healthy adult human. These islets are about 0.2 mm in diameter and are separated from the surrounding pancreas by a thin fibrous connective tissue capsule.
The alpha cells and the beta cells are found in the islet of Langerhans and are responsible for different processes. The alpha cell, also known as the α-cell, is an endocrine cell that is responsible for synthesizing and secreting the peptide hormone glucagon, which elevates the glucose levels in the blood. These cells make up 33-46% of the human islet cells in the body.
In order to elevate the glucose levels in the blood, the glucagons bind themselves to receptors on hepatocytes (liver cells) or kidney cells. The binding results in activating an enzyme known as glycogen phosphorylase inside the hepatocyte. This enzyme hydrolyses glycogen to glucose.
The beta cell, also written as β-cell, is an endocrine cell that is responsible for the production, storage and release of insulin. Insulin is a hormone that is responsible for reducing the blood glucose concentration in the blood. Another role of beta-cells, in addition of producing and storing insulin is to respond quickly to spikes in blood glucose concentrations and release insulin to reduce the concentration. In addition to insulin, the beta cells also produce other hormones such as C-peptide and Amylin. C-peptide helps to prevent neuropathy and other vascular deterioration related symptoms of diabetes mellitus, while amylin is responsible for slowing down the rate at which glucose enters the blood stream.
Beta cells make up 65-80% of the cells in the islets. The control of insulin secretion is done by calcium ion channels and ATP sensitive potassium ion channels. The ATP sensitive potassium ion channels are normally open, while the calcium ion channels are closed. When potassium ions diffuse out of their cells, the make the inside of the cell more negative and create a potential difference across the surface membrane. When glucose concentration is high outside the cells, the molecules move into the cell by facilitated diffusion. Since beta cells use glucokinase to catalyze the first step of glycolysis, metabolism only occurs around physiological blood glucose levels and above. Metabolism of the glucose produces ATP, which increases the ATP to ADP ratio.
Image Courtesy: bbruner.org









Comments
Prathiksha
Fri, 02/02/2018 - 01:28
Anonymous
Fri, 01/19/2018 - 22:32
How can "alpha cells make up 33-46%" and "Beta cells make up 65-80% of the cells in the islets"?
Anthony Nicholl
Tue, 07/08/2014 - 03:08
Add new comment