Difference between DSL and ADSL
Key Difference: DSL stands for ‘digital subscriber line’. It is a broad term that a digital high-speed data connection over telephone lines. ADSL stands for ‘Asymmetric digital subscriber line’. It is a type of DSL technology which has different upload and download speeds.
 Today, technology has come to such a place that nearly everything is dependent on technology. However, most of the technology today would be useless without internet. This is where DSL and ADSL come in.
Today, technology has come to such a place that nearly everything is dependent on technology. However, most of the technology today would be useless without internet. This is where DSL and ADSL come in.
DSL stands for ‘digital subscriber line’. It is a broad term that a digital high-speed data connection. It utilized the same writing as a regular telephone line, however it can also be modified to use cable wiring.
As telephone line only transmit a limited spectrum of signals, i.e. between 20 Hertz to 20,000 Hertz, the frequencies that transmit voice, DSL can utilize the remaining frequencies to transmit data. In order to do this, the consumer typically needs to install a DSL filter, also known as a splitter, on the telephone line which separates the data part from the telephony part. Consumers also need a DSL modem which converts the signal sent on the telephone line to a usable data signal.
The bit rate of consumer DSL services typically ranges from 256 kbit/s to over 100 Mbit/s downstream, i.e. towards the consumer. However, the speed decreases the further away the customer is located from the provider. Hence, one customer may get a speed of 100 Mbit/s, whereas the other may only get 256 kbit/s.
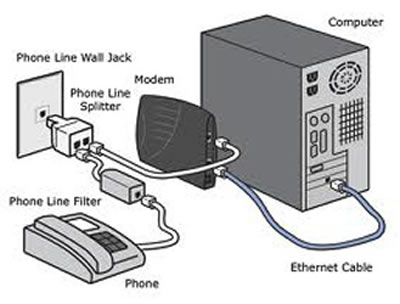 ADSL stands for ‘Asymmetric digital subscriber line’. It is a type of DSL technology; in fact it is the most common and popular type of DSL technology used. ADSL transmits data over copper telephone lines, which is generally faster than a conventional voiceband modem in DSL.
ADSL stands for ‘Asymmetric digital subscriber line’. It is a type of DSL technology; in fact it is the most common and popular type of DSL technology used. ADSL transmits data over copper telephone lines, which is generally faster than a conventional voiceband modem in DSL.
ADSL is named as such because the Bandwidth and bit rate are asymmetric; what this means is that they are greater when geared downstream, i.e. towards the customer, rather than upsteam, i.e. geared towards the provider. Hence, it results in a greater download speed than upload speeds.
However, DSL and ADSL have been steadily falling out of favor and are quickly being labeled as outdated technology. It is being replaced by cable modem, fiber, wireless, and satellite, all which are generally faster in comparison and hence preferable. Additionally, telephone lines themselves are falling into disuse due to the advent of cellular technology. Despite of this, ADSL is still technically considered to be the most commonly utilized technology for broadband internet access, especially in some parts of the world. However, for how long will that be is anyone’s guess.
Comparison between DSL and ADSL:
|
|
DSL |
ADSL |
|
Type of |
Network connection |
DSL Network connection |
|
Stands for |
Digital Subscriber Line |
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line |
|
Provides |
Internet connection |
Internet connection |
|
Signal |
Sends signal over telephone wires |
Sends signal over telephone wires |
|
Devices needed |
|
|
|
Network Speed |
256 kbit/s to over 100 Mbit/s |
256 kbit/s to over 100 Mbit/s |
|
Download speed and Upload speed |
Both are usually the same |
Both are different. Down speed is much faster than Up speed. |
Reference: Wikipedia (DSL and ADSL), Simple Wikipedia, Reference, Livewire (DSL and ADSL) Image Courtesy: myrateplan.com, cio.com








Comments
kwabena wilsom
Wed, 10/04/2017 - 18:45
Good describe
Sun, 07/16/2017 - 14:55
Add new comment