Difference between Sepsis and Infection
Key Difference: An infection is a phenomenon or condition which is caused by invasion of microorganisms or germs into the body. It can be limited to a body region or can be widespread. Sepsis is the body’s response to an infection. It is generally associated with inflammatory response and eventually organ dysfunction and/or failure. Thus, if an infection is left untreated or not treated properly then an infection can often progress to sepsis.
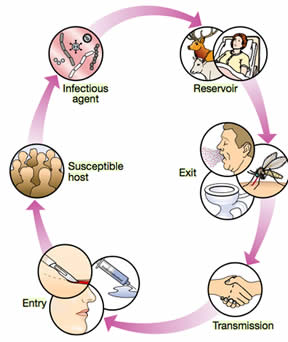 An infection is actually a process in which pathogens like bacteria, virus and fungi enter into the body and get attached to cells. It is actually a host's response to the presence of these types of microorganisms. These organisms have the capability to cause illness, however in many cases the person does not get sick with them. An organism which causes infection is known as an infectious agent.
An infection is actually a process in which pathogens like bacteria, virus and fungi enter into the body and get attached to cells. It is actually a host's response to the presence of these types of microorganisms. These organisms have the capability to cause illness, however in many cases the person does not get sick with them. An organism which causes infection is known as an infectious agent.
The organisms that are capable of causing illness are found everywhere. They can be found in air, water, food, etc. The means of transmission for an infection can be bloodborne, airborne, droplet, contact, etc. It is important to mention that microorganisms that reside naturally in the body are not considered as infections. Infection requires three main elements to occur – a source of the infectious agent, a mode of transmission and a susceptible host.
Infections are generally mild and many times does not require any serious medical treatment. However, there is always a possibility of long term effects, and therefore every infection must be controlled the way serious infections are treated.
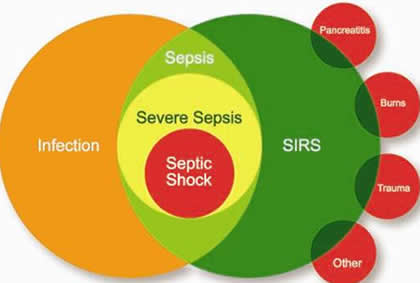 Sepsis is a serious complication of an infection. It is the inflammatory response to infection. Sepsis is capable of affecting the whole body including the organs. Septacaemia is also related to sepsis as it is caused due to a bacterial infection of the blood, whereas sepsis can be caused by viral or fungal infectionsalso.
Sepsis is a serious complication of an infection. It is the inflammatory response to infection. Sepsis is capable of affecting the whole body including the organs. Septacaemia is also related to sepsis as it is caused due to a bacterial infection of the blood, whereas sepsis can be caused by viral or fungal infectionsalso.
Sepsis is basically a body’s reaction to infection. It is generally associated ith severe sepsis or septic shock, and therefore it is taken very seriously. It is a life threatening situation which arises when body tries to respond the infection in such a way that it starts injuring body’s own tissues and organs.
A person is considered septic if he meets the necessary criteria described in SIRS Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. These criteria have been described by many medical societies and still are modified by medical groups. Uncomplicated sepsis caused by flu and other viral infections are put in the category of uncomplicated sepsis and therefor generally do not require any hospital treatment.
As sepsis is also caused due to infections, both need to be controlled by taking same precautions like – standard precautions which deals with basic level of infection control mechanisms. Precautions should also be taken while being in direct orindirect contact with contaminated body fluids, equipment or environment. Airboune precautions include use of procedures like nebulizing, suctioning, etc.
Comparison between Sepsis and Infection:
|
|
Sepsis |
Infection |
|
Definition |
Sepsis is the body’s response to an infection. (Documented infection together with 2 or more SIRS criteria).
|
An infection is a phenomenon which is caused by invasion of microorganisms or germs into the body. |
|
Symptoms |
Signs and symptoms fulfill at least two of the following criteria of a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS):
|
Symptoms of an infection may differ from one to another depending on the type of disease – Some signs which are commonly found are –
|
|
Cause |
Sepsis may develop from any type of infection, the ones that most frequently cause the disease are bronchopulmonary, abdominal, and urinary tract infections. |
Caused by organisms — such as bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. |
|
Diagnosis |
To diagnose sepsis, several tests may be carried out including:
|
|
|
Treatment |
|
|
Image Courtesy: vdilab.com, quizlet.com









Add new comment