Difference between Tumor and Cancer
Key difference: The human body is complex. At times, the cells of the body do not act in the way that they should. They may start to divide and grow uncontrollably. These extra cells tend to get stuck together and start forming small lumps or growths. Over time, more and more cells start to stick to these lumps causing them to further grow in size. These lumps or growths are called tumors or a neoplasm. A tumor can be benign (not cancerous), pre-malignant (pre-cancerous), or malignant (cancerous).
 Tumor and Cancer are two words that no one wants to hear. Both seem to send a sane person into a panicked frenzy, but there is some good news: not all tumors aim to kill you and many forms of cancers are effectively treatable. But what is the difference between the two?
Tumor and Cancer are two words that no one wants to hear. Both seem to send a sane person into a panicked frenzy, but there is some good news: not all tumors aim to kill you and many forms of cancers are effectively treatable. But what is the difference between the two?
The human body is complex. At times, the cells of the body do not act in the way that they should. They may start to divide and grow uncontrollably. These extra cells tend to get stuck together and start forming small lumps or growths. Over time, more and more cells start to stick to these lumps causing them to further grow in size. These lumps or growths are called tumors or a neoplasm. These tumors may be solid or fluid-filled.
However, a tumor does not equate to cancer. A tumor can be benign (not cancerous), pre-malignant (pre-cancerous), or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors are mostly harmless, but some may have slightly negative health effects, such as pushing against vital organs or blood vessels (known as "mass effect") or they may lead to overproduction of certain hormones. Due to this, benign tumors should still be removed. This can be mainly done via surgery.
A pre-malignant tumor or a pre-cancerous tumor is a growth that is probably harmless at the moment but does have a significantly increased risk of cancer. This means that if the tumor is left untreated, it may lead to the conditions that may lead to cancer
A malignant tumor is a tumor that is considered to be cancer. In cancer, the cells divide and grow uncontrollably. However, instead of sticking together in a singular place, as in the case of a benign tumor, these cells go all over the place and create malignant tumors in various places. Hence, cancer is not just the presence of a single malignant tumor but many.
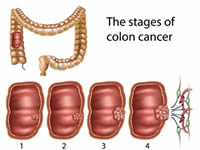 In order to treat these malignant tumors, surgery is required to remove the tumors, in addition to chemo or radiotherapy. These treatments aim to control and eradicate the cancerous cells which will continue to replicate and create tumors. These cells have the ability to spread to various parts of the body through the lymphatic system or bloodstream.
In order to treat these malignant tumors, surgery is required to remove the tumors, in addition to chemo or radiotherapy. These treatments aim to control and eradicate the cancerous cells which will continue to replicate and create tumors. These cells have the ability to spread to various parts of the body through the lymphatic system or bloodstream.
Tumors can affect any part of the body, but usually only the cancerous tumors tend to spread to other parts of the body. There are in fact over 200 different known cancers that afflict humans.
It is still unsure as to why some tumors are not cancerous, while some are. However, there are many things are known to increase the risk of cancer, including tobacco use, certain infections, radiation, lack of physical activity, obesity, and environmental pollutants. These can directly damage genes or combine with existing genetic faults within cells to cause the disease. Some types of cancers are known to be hereditary.
There are ways to detect the presence of cancer. These include the presence of certain signs and symptoms, screening tests, or medical imaging. When the cancer is detected, it is diagnosed by microscopic examination of a tissue sample, also known as a biopsy. Once the type of cancer is known, appropriate treatments are undertaken. The chances of surviving the disease vary by the type and location of the cancer, as well as the extent of disease at the start of treatment. It is estimated that in 2007, 13% of all human deaths worldwide were caused by cancer. That amounts to 7.9 million deaths.
Image Courtesy: skinblemishcare.wordpress.com, earthtimes.org








Add new comment