Difference between Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning
Key difference: Artificial Intelligence is the computer’s attempt to imitate human intelligence. Whereas Machine Learning focuses on analyzing large chunks of data and learning from it. Deep learning, on the other hand, allows the computer to actually learn and differentiate and make decisions like a human.
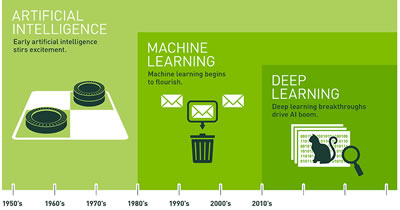 Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are now buzzwords in the industry. They especially have an impact in the business industry and specifically in the information technology center. However, to a layman these terms can be quiet confusing. Adding to the confusion is the fact that these terms are interrelated, which makes it ever harder to tell them apart.
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are now buzzwords in the industry. They especially have an impact in the business industry and specifically in the information technology center. However, to a layman these terms can be quiet confusing. Adding to the confusion is the fact that these terms are interrelated, which makes it ever harder to tell them apart.
While some people may be afraid that this technological advancement may lead to the end of the world, there is no denying that they do have significant implications in today’s world. It is artificial intelligence that had allowed for the development of self-driving cars, face recognition, web search, industrial robots, missile guidance, and even tumor detection. Without artificial intelligence or machine learning, the world would still be back in the dark ages. It is only due to these things that we are moving into a technological advanced future.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not a new concept. It has existed since the 1960s, when it was developed in order to develop computers that would be able to do the things that humans are capable of doing, such as "learning" and "problem solving". One of the most famous examples of Artificial Intelligence is a computer playing chess against a human player. This shows the computer is able to think and plan ahead.
The current scopes of Artificial Intelligence include understanding human speech, competing at a high level in strategic game systems, such as chess and Go, as well as, self-driving cars, intelligent routing in content delivery networks, military simulations, and interpreting complex data.
Machine Learning, on the other hand, is a subset of Artificial Intelligence. It attempts to develop a machine that can act without programming. In AI, a machine is typically programmed to do something. While the machine in this scenario is smart, it does not learn. The intelligence is programmed into the computer, whereas machine learning allows the computer to learn something new, something that it was not programmed to do.
The machine or computer learns via the process of data mining. When new data is fed into the computer, the computer will analyze the data and absorb the information. It can then use that data to detect patterns in data and then adjust program actions accordingly. An example of this would be its use in Facebook's News Feed. Here, the unsupervised algorithms observe user actions and their patterns to decide which content will be more relevant for the user. It will then show the user more relevant content, which will be ranked higher on their News Feed.
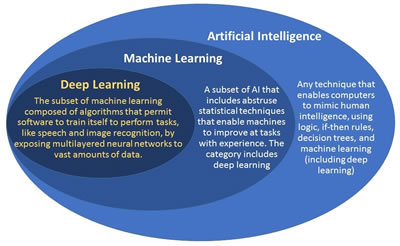 Similarly, deep learning is a subset of machine learning. In machine learning, the computer is able to recognize patters, understand speech, and make inferences and predictions. Deep learning takes the ability of the computer to learn a step further. Here, the computers are able to actually learn and know things, rather than just compare data. Computers are able to learn the characteristics of something like a face. Deep learning can also be used to solve real-world problems by tapping into neural networks that simulate human decision-making.
Similarly, deep learning is a subset of machine learning. In machine learning, the computer is able to recognize patters, understand speech, and make inferences and predictions. Deep learning takes the ability of the computer to learn a step further. Here, the computers are able to actually learn and know things, rather than just compare data. Computers are able to learn the characteristics of something like a face. Deep learning can also be used to solve real-world problems by tapping into neural networks that simulate human decision-making.
Hence, it can be said that basically, Artificial Intelligence is the computer’s attempt to imitate human intelligence. Whereas Machine Learning focuses on analyzing large chunks of data and learning from it. Deep learning, on the other hand, allows the computer to actually learn and differentiate and make decisions like a human.
Comparison between Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning:
|
|
Artificial Intelligence |
Machine Learning |
Deep Learning |
|
Definition (TechTarget) |
The simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems |
A type of artificial intelligence (AI) that provides computers with the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed |
An aspect of artificial intelligence (AI) that is concerned with emulating the learning approach that human beings use to gain certain types of knowledge |
|
Description |
An umbrella term that encompasses everything from robotic process automation to actual robotics |
Focuses on the development of computer programs that can change when exposed to new data. |
A way to automate predictive analytics, where the machine learns from a set of data and use it to make predictions. |
|
Includes |
Learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using the rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction |
Data mining, extraction of data, analysis of data, and using that data to detect patterns in data and adjust program actions accordingly. |
Data mining, data extraction, data classification, data implementation |
|
Scope |
Limited scope. Machines are programmed for a particular task and they typically cannot do anything other than follow programming. |
Large scope. Machines can learn to infer and make predictions by analyzing large sets of data. |
Unlimited scope. Machine can learn to emulate human intelligence and decision making by learning and analyzing large sets of data. |
|
Capabilities |
Development of self-driving cars, face recognition, web search, industrial robots, missile guidance, and even tumor detection |
Text-based searches, fraud detection, spam detection, handwriting recognition, image search, speech recognition, Street View detection, and translation |
Computer vision, automatic speech recognition, natural language processing, audio recognition and bioinformatics |
|
Examples |
IBM's Deep Blue, which beat chess grand master Garry Kasparov at the game in 1996. |
DeepMind's AlphaGo, which in 2016 beat Lee Sedol at Go, by analyzing a large data set of expert moves. |
Automatic Game Playing or Automatic Handwriting Generation |
Reference: TechTarget (Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning), Wikipedia (Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning), NVIDIA, Tech Republic Image Courtesy: nvidia.com, geospatialworld.net









Add new comment