Difference between AWD and 4WD
Key difference: The difference between the two driving systems is based on the usage of all the four wheels of a car. In 4WD system, the driver has the option to power and use all the four wheels or only the two wheels in a system, whereas in AWD system, the driving process is permanently engaged and the driver has no option to disengage the system.
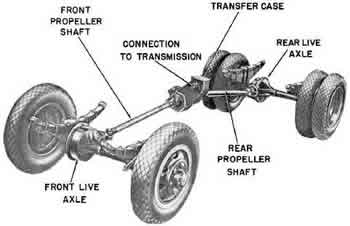 The term 4WD stands for ‘Four Wheel Drive’. It is a convenient system and widely used in all cars as a way to power the tires of a car. It allows all the four wheels to receive torque from the engine.
The term 4WD stands for ‘Four Wheel Drive’. It is a convenient system and widely used in all cars as a way to power the tires of a car. It allows all the four wheels to receive torque from the engine.
The 4WD refers to vehicles which have a transfer case between the front and rear axles. It means that when the system is engaged, the front and rear drive shafts are locked together and cause traction. This system then transfers maximum torque to the axle with the most traction, causing them to move and turn. There are two types of selectable system:
Full-time 4WD
Part-time 4WD
This system allows the driver to switch the mode of driving according to the surface on which he wants to drive the car. It is considered as an ideal system to be installed in a car. With the two different types of 4WD; the part-time 4WD is considered more suitable as it has various features and the car can be driven in slower speed as compared to full-time 4WD. Also, this system is cheap in cost and is considered as ideal to be driven it heavy duty car systems. It lacks the central differential system, which makes the vehicle easier to drive and move. The part-time 4WD allows the driver to alter the driving circumstances according to the requirements, whereas the full-time 4WD makes driving more convenient by giving a range of permanent assistances.

The term AWD stands for ‘All Wheel Drive’. This system has all the wheels powered at all the times. It is used in high and low traction situations without the driver input.
The AWD refers to a drive train system that includes a differential, a mechanical device, between the front and rear drive shafts. This is normally coupled with some sort of anti-slip technology that allows the differentials to spin at different speeds, but still maintain the ability to transfer torque from one wheel to another wheel, in case of loss of traction at that wheel.
This system is a much better choosing option, when buying a vehicle. It is ideal to be used on the road and is more efficient when using or running on road. This system is sure expensive in use; however it has the advantage of being inbuilt, very low in weight and the ability to move freely in all types of roads. Also, they have the quality of driving very smoothly in all weathers, even in the rains and are very popular due to their compatibility.
Comparison between AWD and 4WD:
|
|
AWD |
4WD |
|
Acronym |
It stands for ‘All Wheel Drive’. |
It stands for ‘4 Wheel Drive’. |
|
Definition |
It has a central differential system and thus is designed to power all four wheels at the same time. |
Depending on the type of the system and on the road conditions, it is designed to automatically adjust the power in the front and back wheels. |
|
Gear |
Only high range gearing. |
Low range and high range gearing. |
|
Weather |
It does not help in running the car smoothly in snow and rains. |
It helps to run the car smoothly in snow and rains. |
|
Cost |
It is expensive. |
It is cheap. |
|
Weight |
It is light in weight and consumes less space. |
It is heavy in weight and consumes space. |
|
Types |
It can be automatic or selectable. |
It is part time or full time. |
|
Engine power |
The vehicles deliver 90% of its engine power to the front wheels. More engine power is diverted to rear wheels via viscous coupling, only when the front wheels start to slip. |
It transmits all of its engine power to the rear wheels. The second speed option allows splitting the engine power equally between front and rear wheels. |
|
Differential device |
The option of central differential is available. |
The option of central differential is inbuilt and is not available. |
|
Advantages |
|
|
|
Disadvantages |
|
|
|
Examples |
Pontiac Vibe, Toyota Matrix, Subaru Legacy GT. |
Suzuki SUVs (part time), Mitsubishi Montero (full time). |
Image Courtesy: enginemechanics.tpub.com, caradvice.com.au









Add new comment