Difference between NAS and SAN
Key Difference: NAS, short for Network-attached storage is a file level computer data storage connected to a computer network that provides access to clients. SAN, short for Storage-area Network, is a dedicated network that allows multiple users to access block level data storage.
 Storage systems play a crucial part in any organization’s computers. Any company running a business requires a storage area where data can be stored; this is most commonly known as the server. Servers store combined data that can be accessed to anyone that connects their computer to the server. However, the amount of space allowed on the server is limited, which requires purchasing multiple servers; which can becomes a hassle. So, say someone wants to extend the amount of data on the server they can use two different types of storage networks: SAN and NAS. These two network types are often confused as they seem familiar at first glance. However, they are very different from each other.
Storage systems play a crucial part in any organization’s computers. Any company running a business requires a storage area where data can be stored; this is most commonly known as the server. Servers store combined data that can be accessed to anyone that connects their computer to the server. However, the amount of space allowed on the server is limited, which requires purchasing multiple servers; which can becomes a hassle. So, say someone wants to extend the amount of data on the server they can use two different types of storage networks: SAN and NAS. These two network types are often confused as they seem familiar at first glance. However, they are very different from each other.
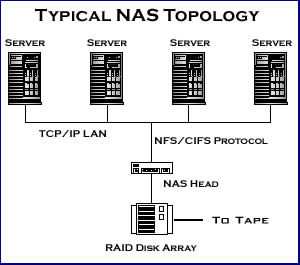
NAS, short for Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file level computer data storage connected to a computer network that provides access to clients. NAS only works at a file-level, which means it will come off as a sharing folder for the people who are accessing this storage system. NAS is manufactured as a computer appliance that is built as a specialized computer whose main purpose is to store and serve files. Advantages of using a NAS include faster data access, easier administration and simple configuration. NAS systems are networked appliances which contain one or more hard drives, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID.
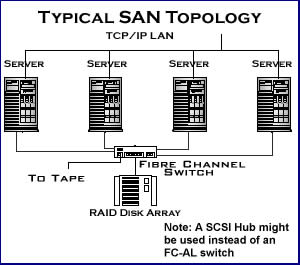 SAN, short for Storage-area Network, is a dedicated network that allows multiple users to access block level data storage. SAN stores data in a block level, which means it provided multiple hard drives within one unit. These units are known as Local Unit Numbers or LUNs. Each of these blocks are seen as a hard drive by the server. A SAN usually has its own network of storage devices that are commonly not accessible through the local area network by other devices. Each server can only access one LUN. However, one benefit of a SAN is the ability of SAN to transfer un-used data from one server to another server. This reduces the need for buying multiple storage units.
SAN, short for Storage-area Network, is a dedicated network that allows multiple users to access block level data storage. SAN stores data in a block level, which means it provided multiple hard drives within one unit. These units are known as Local Unit Numbers or LUNs. Each of these blocks are seen as a hard drive by the server. A SAN usually has its own network of storage devices that are commonly not accessible through the local area network by other devices. Each server can only access one LUN. However, one benefit of a SAN is the ability of SAN to transfer un-used data from one server to another server. This reduces the need for buying multiple storage units.
Both of these servers are different from each other in many ways. SAN is commonly useful for long-distance storage, while NAS is useful for local storage. NAS saves at file level, while SAN saves at block level. SANs are designed to provide high performance, flexibility in use and scalable storage environment. SANs can use the already available network switch or iSCSI for connecting to a server. NAS allows clients to access the data from anywhere in the building if they are logged onto the server. Purchasing NAS or SAN depends on the type of operation that is being run and the cost. NAS is comparatively cheaper than SAN.
|
|
NAS |
SAN |
|
Full Form |
Network-attached Storage |
Storage-area Network |
|
Definition |
NAS is a file level computer data storage that is connected to a computer network that is providing access to clients. |
SAN is a dedicated network that allows multiple users to access block level data storage. |
|
Level of data storage |
File level |
Block Level |
|
Connection |
Almost any machine that can connect to a LAN can use NFS, CIFS or HTTP protocol to connect to a NAS and share files. |
Only server class SCSI or Fiber Channel can connect to SAN. |
|
How it identifies data |
Identifies data by file name and byte offsets, transfers file data or file meta-data and handles security, user authentication, file locking |
A SAN addresses data by disk block number and transfers raw disk blocks. |
|
Sharing of information |
allows greater sharing of information especially between disparate operating systems |
File Sharing is operating system dependent and does not exist in many operating systems. |
|
Managed by |
Managed by NAS head unit. |
File Systems is managed by servers. |
|
Back Ups and Mirrors |
Are done on files, not blocks, for a savings in bandwidth and time |
Require a block by block copy, even if blocks are empty. A mirror machine must be equal to or greater in capacity compared to the source volume. |
Images Courtesy: nas-san.com









Add new comment