Difference between Pipe and Tube
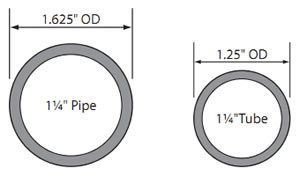
Key Difference: Pipes are hollow cylinders that are found in everyday bathrooms and kitchens. Tubes are long cylinders that are used for moving fluids as well as protecting wires or cables. Pipes are measured using the inside diameter. Tubes are most often specified by the OD and wall thickness.
 Pipes and tubes are common words that are heard daily as they are found in various places around the house. These two words are commonly mistaken as the same thing. A tube is often assumed to be a pipe; however, this is incorrect. Pipes and tubes are used for different things and are though they may look the same they are measure differently.
Pipes and tubes are common words that are heard daily as they are found in various places around the house. These two words are commonly mistaken as the same thing. A tube is often assumed to be a pipe; however, this is incorrect. Pipes and tubes are used for different things and are though they may look the same they are measure differently.
Pipes are hollow cylinders that are found in everyday bathrooms and kitchens. These are mainly used to transfer substances from one place to another. They are found in a variety of thickness and size. The small ones can be found in the sink of the bathroom, while bigger ones are found connecting the toilets. Pipes are used to convey substances such as liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders, masses of small solids, etc. Tubes are long cylinders that are used for moving fluids as well as protecting wires or cables. Tubes are not limited to usage in the kitchen and bathroom and are found in many places inside the house including electrical outlets. The term ‘tube’ is also applied to non-cylindrical sections such as square or rectangular tubing.
Although in general usage these words can be used interchangeably; these two differ in engineering and industry. Depending on the application, pipes are generally specified by a nominal diameter with a constant outside diameter (OD) and a schedule that defines the thickness. Pipes are measured using the inside diameter. Tubes are most often specified by the OD and wall thickness, but may be specified by any two of OD, inside diameter (ID), and wall thickness.
Both pipes and tubes are rigid in nature, while others such as hosepipes are flexible and can be curled. A tube and pipe may be specified by standard pipe size designations or by nominal outside or inside diameter and/or wall thickness. There are three classes of manufactured tubing: seamless, as-welded or electric resistant welded (ERW), and drawn-over-mandrel (DOM).
Image Courtesy: jd2.com.au







Add new comment