Difference between Primary Teeth and Permanent Teeth
Key Difference: Primary teeth are the first set of teeth possessed by human beings in his lifecycle. Permanent teeth are the second set of teeth possessed by human beings. Temporary teeth are 20 in number, whereas permanent teeth are usually 32 in number. Primary or milk teeth retains space for the child’s future permanent teeth. There are many differences between primary and permanent teeth in context to morphology, etc.
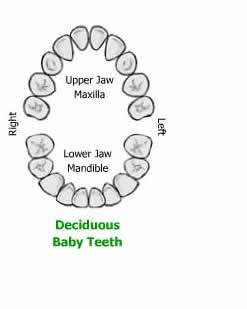 A human being possesses two types of sets of teeth in a lifetime – Primary and Permanent teeth. Primary teeth are also known as baby, milk, deciduous or lacteal teeth. The term deciduous means ‘to fall off’. These teeth are the first sets of teeth and are twenty in number (10 in each jaw). These teeth start erupting since the age of six months and generally keep on erupting until three years of age. These teeth help in retaining space which is later occupied by permanent teeth.
A human being possesses two types of sets of teeth in a lifetime – Primary and Permanent teeth. Primary teeth are also known as baby, milk, deciduous or lacteal teeth. The term deciduous means ‘to fall off’. These teeth are the first sets of teeth and are twenty in number (10 in each jaw). These teeth start erupting since the age of six months and generally keep on erupting until three years of age. These teeth help in retaining space which is later occupied by permanent teeth.
Primary teeth can be divided into three categories in each jaw – four incisors, two canines and four molars. The age of six to twelve is marked by losing the deciduous teeth and gaining permanent teeth. This time period is also known as mixed detention. Permanent teeth erupt through the gum and gradually the 20 primary teeth gets replaced by 32 permanent teeth, including 16 in each jaw.
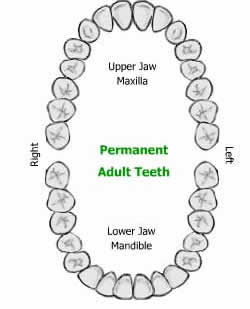 Permanent teeth erupts just beneath the roots of milk teeth and when a deciduous tooth prepares itself to fall out, its root starts dissolving. Permanent teeth are also known as adult or seconday teeth. Permanent teeth consist of 4 third molars (also called wisdom teeth), 4 second molars, 4 first molars, 4 second bicuspids, 4 first bicuspids, 4 cuspids, 4 lateral incisors and 4 central incisors.
Permanent teeth erupts just beneath the roots of milk teeth and when a deciduous tooth prepares itself to fall out, its root starts dissolving. Permanent teeth are also known as adult or seconday teeth. Permanent teeth consist of 4 third molars (also called wisdom teeth), 4 second molars, 4 first molars, 4 second bicuspids, 4 first bicuspids, 4 cuspids, 4 lateral incisors and 4 central incisors.
Primary teeth are smaller in size and crown dimensions. Primary teeth are also lighter in color and the buccolingual diameter of primary molar teeth is also less than in comparison to permanent teeth.
Primary crowns are wider in the mesial-to-distal dimension than crown length of permanent teeth. Enamel and dentin are thinner in milk teeth. There is also a difference in shape. The cusps in deciduous teeth are more pointed and the crown are bulbous, whereas in permanent teeth, the cusps are blunt and crown are not bulbous.
Comparison between Primary Teeth and Permanent Teeth:
|
|
Primary Teeth |
Permanent Teeth |
|
Definition |
Primary teeth are the first set of teeth possessed by human beings in his lifecycle. |
Permanent teeth are the second set of teeth possessed by human beings. |
|
Overall size and crown dimension |
Smaller |
Bigger |
|
Color |
Less pigmented, more whiter |
More pigmented, less whiter |
|
Clinical crowns |
Shorter |
Longer |
|
Roots of front primary teeth |
Narrower |
Wider |
|
Pulp chamber |
Larger as compared to crown |
Smaller as compared to crown |
|
Root anatomy |
Thin, slender, flared |
Thicker, not flared |
|
Accessory canals |
Present frequently in furcation area and roots |
Comparatively less in number |
|
Number of teeth |
20 |
Usually, 32 |
|
Types |
2 incisors, 1 canine and 2 molars in each quadrant. There are no premolars |
2 incisors, 1 canine 2 premolars and 3 molars in each quadrant |
|
Eruption |
Starts at 6 months and continues till three years. The teeth are exfoliated by 13 years |
Eruption starts at 6 years and continues till 25 years or more. They tend to stay in oral cavity for a longer time |
|
Placement |
Perpendicularly in jaws |
Obliquely in jaws |
Images Courtesy: gtchild.co.uk








Add new comment