Difference between Tissues and Organs
Key Difference: Tissues are an organization level between cells and organs. Tissues are made up of a group of similar cells and from the same origin that carry out the same function. Organs comprise a group of similar tissues that perform a similar function. The organs work together and are responsible for the daily functioning of an organism’s body.
All living things are either made up of single cells or multiple cells. The cell is the smallest organism that is living and is capable of growth, development, respiration, excretion and reproduction. Almost all organisms, except protozoans are multicellular. The cells combine together to make tissues, which make up organs. Cells, tissues and organs are responsible for performing the basic functions of a living organism which keeps the organism alive.
 Tissues are an organization level between cells and organs. Tissues are made up of a group of similar cells and from the same origin that carry out the same function. The study of tissues is known as histology. The tissues that are found in animals can be grouped into four basic types: connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial. Connective tissues are fibrous tissues, which are responsible for shaping organs and holding them in place. Muscle tissues are responsible for producing force and movement in the internal organs. Nervous tissues are found in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system; they are responsible for forming the brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves and spinal nerves. A function of nervous tissue is to transmit messages from the brain to the other organs in form of electrical impulses. Epithelial tissues are cells that cover the organ surfaces, such as skin. Tissues can also be found in plants which can be broadly categorized into three systems: the epidermis, the ground tissue, and the vascular tissue.
Tissues are an organization level between cells and organs. Tissues are made up of a group of similar cells and from the same origin that carry out the same function. The study of tissues is known as histology. The tissues that are found in animals can be grouped into four basic types: connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial. Connective tissues are fibrous tissues, which are responsible for shaping organs and holding them in place. Muscle tissues are responsible for producing force and movement in the internal organs. Nervous tissues are found in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system; they are responsible for forming the brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves and spinal nerves. A function of nervous tissue is to transmit messages from the brain to the other organs in form of electrical impulses. Epithelial tissues are cells that cover the organ surfaces, such as skin. Tissues can also be found in plants which can be broadly categorized into three systems: the epidermis, the ground tissue, and the vascular tissue.
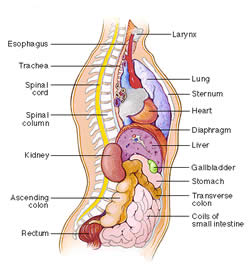
Organs comprise a group of similar tissues that perform a similar function. The organs work together and are responsible for the daily functioning of an organism’s body. The study of human organs is known as anatomy. A human body is made up of eleven distinct types of organ systems: cardiovascular system, digestive system, endocrine system, excretory system, immune system, integumentary system (skin, hair, and nails), muscular system, nervous system, reproductive system, respiratory system and skeletal system. In single-cell organisms, the functional analogues of organs are known as organelles. In plants, the organ systems can be divided into vegetative and reproductive; vegetative organs are roots, stems and leaves, while reproductive organs differ depending on the species.
|
|
Tissue |
Organs |
|
Definition |
Group of likeminded cells. |
A group of likeminded tissue group together to form organs, which is responsible for performing major functions of the body |
|
Components |
Similar cells |
Similar tissues |
|
Types |
Epithelial tissue, nerve tissue, muscle tissue, and connective tissue. |
Heart, lungs, stomach, intestine, bladder, etc |
|
Developmental processes |
Tissue repair through regeneration and fibrosis |
Tissues repair the organs |
|
Functions |
Group of similar cells come together to perform a similar function and to form organs. |
There are various organ systems in our body that perform basic functions such as pumping blood, breaking down food, breathing, etc. |
Image Courtesy: pathologyoutlines.com, i-base.info









Comments
Mudit
Tue, 08/29/2017 - 20:48
Mudit
Tue, 08/29/2017 - 20:47
EAST R WEST UR THE BEST..............
IRON MAN
Tue, 06/09/2015 - 19:30
Thank for the help
clara
Tue, 01/13/2015 - 01:07
science is the best
shayne
Thu, 09/11/2014 - 21:41
Add new comment