Difference between DNA and Chromosome
Key Difference: DNA, short for Deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions that is used for the development and functioning of cells in a living organism and many viruses. Chromosomes are basically organized structure of DNA and protein cells that are found in a cell.
Chromosomes and DNA are an important part that sustains the life and growth of living organisms. These two are related; however they are not the same. These two differ from each other in various ways. DNA refers to molecules that encode the genetic information of living organisms, while chromosomes are tightly packed DNA strands.
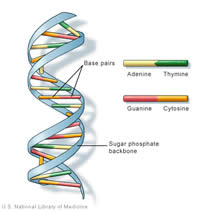 DNA, short for Deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions that is used for the development and functioning of cells in a living organism and many viruses. In addition to protein and RNA, DNA is an essential macromolecule for the existence of all living organisms. The genetic information is coded as a sequence of nucleotides such as guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The main purpose of a DNA is to tell each cell what proteins it has to make. The type of protein a cell makes determines the cell’s function. DNA is inherited from parent to offspring, which is why parents and children share similar traits. Each person’s cell has about 46 double stranded DNA that is a result of the one set of chromosome that a person acquires from each parent.
DNA, short for Deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions that is used for the development and functioning of cells in a living organism and many viruses. In addition to protein and RNA, DNA is an essential macromolecule for the existence of all living organisms. The genetic information is coded as a sequence of nucleotides such as guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The main purpose of a DNA is to tell each cell what proteins it has to make. The type of protein a cell makes determines the cell’s function. DNA is inherited from parent to offspring, which is why parents and children share similar traits. Each person’s cell has about 46 double stranded DNA that is a result of the one set of chromosome that a person acquires from each parent.
The DNA molecule has a double helix shape, which resembles a ladder that is twisted into a spiral shape. Each rung of the ladder has a pair of nucleotides that stores the information. The backbone of the DNA is made up of alternating sugars (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups, from which the DNA gets its name. The nucleotides are attached to the sugar in a special formation. The adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G) nucleotides always form A-T and C-G pairs, though they could be found in any order on the DNA. The Adenine and thymine pair up to make two hydrogen bonds, while cytosine and guanine make three hydrogen bonds. The different order is how the DNA can write ‘codes’ out of the ‘letters’ telling the cells what duties to perform.
The encoded information is read using the genetic code, which specifies the sequence of the amino acids in within proteins. The code is read by a transcription process, in which the DNA is copied into related nucleic acid RNA. Within the cells, DNA is placed in chromosomes that are divided during cell division. Each cell has its own complete set of chromosome. Eukaryotes store most of their DNA inside the cell nucleus and some other DNA in organelles. Prokaryotes store their DNA in the cytoplasm.
 Chromosomes are basically organized structure of DNA and protein cells that are found in a cell. It is a single piece of coiled DNA that contains many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. It also contains DNA-bound proteins that allow it to control its functions. DNAs are made up of 100,000 to over 3,750,000,000 nucleotides which are either in linear form of circular form depending on the organism. This form is then packed with proteins and is formed into chromosomes. A human being has 23 chromosomes from each parent, making it 46 chromosomes per cell. Human chromosomes are approximately s6 µm long, a packing ratio of 8000:1.
Chromosomes are basically organized structure of DNA and protein cells that are found in a cell. It is a single piece of coiled DNA that contains many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. It also contains DNA-bound proteins that allow it to control its functions. DNAs are made up of 100,000 to over 3,750,000,000 nucleotides which are either in linear form of circular form depending on the organism. This form is then packed with proteins and is formed into chromosomes. A human being has 23 chromosomes from each parent, making it 46 chromosomes per cell. Human chromosomes are approximately s6 µm long, a packing ratio of 8000:1.
In eukaryotes, nuclear chromosomes are packed by proteins into a condensed structure known as chromatin. This structure allows the DNA to fit inside the cell nucleus. The structure of chromosome and chromatin varies through the cell’s life cycle. During cell division, chromosomes are replicated, divided and successfully passed on to the daughter cells. These chromosomes ensure genetic diversity and survival of their progeny. There are two types of chromosomes: duplicated and unduplicated. Duplicated chromosomes have two identical single linear strands that are joined by centromere, while unduplicated chromosomes are single linear strands.
Chromosomes play a huge part in genetic diversity and are duplicated and split during mitosis and meiosis. If the chromosomes are incorrectly duplicated they go through a process known as chromosomal instability and translocation, where the cell could die or lead to the progression of cancer. The word chromosome is derived from the Greek χρῶμα (chroma, colour) and σῶμα (soma, body), because of them being strongly stained by some dyes.
Image Courtesy: ghr.nlm.nih.gov, le.ac.uk







Add new comment