Difference between Mutation and Birth Defect
Key Difference: A birth defect is a condition that exists when a baby is born. It can occur at the time of the birth itself, or before birth, in the womb. A mutation is a type of birth defect. It is a change in the DNA sequence that leads to changes within the organism.
 Both mutation and birth defect are things that no parents what to think about, let alone deal with. However, sadly in this world these things do happen, and all parents to be should know what they are and how they differ from each other, as well as the impact that it can have on the baby and the family as a whole.
Both mutation and birth defect are things that no parents what to think about, let alone deal with. However, sadly in this world these things do happen, and all parents to be should know what they are and how they differ from each other, as well as the impact that it can have on the baby and the family as a whole.
The main difference between Mutation and Birth Defect is that mutation is a type of birth defect. A birth defect is a condition that exists when a baby is born. It can occur at the time of the birth itself, or before birth, in the womb. A birth defect is also known as congenital disease or congenital disorder.
There are many different types of birth defects, and each can be caused by a multitude of factors. Any susbtance that causes birth defects is called a teratogen. The teratogen could be genetic, such as genetic mutation or chromosomal abnormality, or environmental factors, such as nutritional depervation, alcohol use, chemical mutagens, age, and smoking habits.
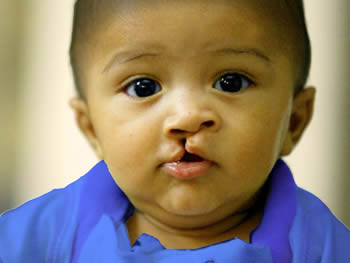
There are many different types of birth defects. They can be physical, such as cleft palate, shortness of the 4th metacarpal or metatarsal bones, congenital heart disease, etc., or mental, leading to disability or developmental issues. In fact, there are more than 4,000 different types of birth defect. Some birth defects do not need treatment and do have that much on an impact on the life of the child; however, some may require medical or surgical treatment, while others can be fatal.
A mutation is a type of birth defect. While most people refer to mutations as a bad thing, it may not necessarily be so. In fact, if it weren’t for a series of right mutations, we as modern humans would not even exist. Mutations allow us to change and adapt. However, sometimes those changes don’t work, and they hamper the existence of the organism, i.e. they can be problematic or even fatal.

A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. This change might be minor and have no impact within the organism, or it can be major leading to anomalies or even death. Mutations occur in the DNA within a single. This happens when the cell copies its DNA when it splits into two. Errors that occur during this process are called mutations. The most common types of mutations are when some information is replaced with another, or at times some information is added or deleted. If the change is minor, the cell is usually able to repair most of the changes. However, if the change is major then it can lead to changes such as but not limited to blue eyes, green eyes, red hair, blonde hair, as well as numerous diseases, such as Down Syndrome.
However advancements in science and technology have made it possible for doctors to check for birth defect within the womb as the baby is developing, so that the necessary precautions can be take for the health of the baby.
Comparison between Mutation and Birth Defect:
|
|
Mutation |
Birth Defect |
|
Description |
Mutation is a natural process that changes a DNA sequence, which leads to changes in the body. |
Birth defect is a condition existing at or before birth regardless of cause. |
|
Definition (Merriam-Webster) |
A change in the genes of a plant or animal that causes physical characteristics that are different from what is normal. |
A physical or biochemical defect that is present at birth and may be inherited or environmentally induced. |
|
Type of |
Birth Defect |
Disorder |
|
Occurs |
Usually at the time of conception, except in the case of cancer. |
Most commonly in the first trimester. |
|
Types |
Small-scale mutations, such as those affecting a small gene in one or a few nucleotides. Large-scale mutations in chromosomal structure.
|
|
|
Causes |
|
|
Image Courtesy: baby.healthguru.com, gallery4share.com









Add new comment