Difference between Sprain and Strain
Key Difference: Sprain and strain are two common injuries. Sprains occur due to stretching or tearing of ligaments, whereas strains occur due to stretching and tearing of muscles or tendons. They have similar signs and symptoms.
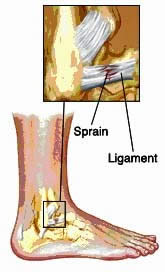 Many people use sprain and strain interchangeably. However, they both refer to two different types of common injuries related to muscoskeletal system. A sprain is that kind of injury in which a ligament or a joint capsule gets tear or stretched.
Many people use sprain and strain interchangeably. However, they both refer to two different types of common injuries related to muscoskeletal system. A sprain is that kind of injury in which a ligament or a joint capsule gets tear or stretched.
Ligament is a thick and strong fibrous tissue which connects the end of one bone with another. They provide the support to body joints. Due to this injury, joint can become instable. One should not try to force a joint beyond its capability of motion like in case of turning the ankle beyond its limit. Pain and inflammation are common symptoms of a sprain. However, in severe type of injury, one may not be able to even move a limb.
Severity of a sprain is defined by three degrees ranging from mild to most severe.
- First degree – it is the mildest of all with little tearing, swelling or pain. Joint stability is not affected much.
- Second degree – Most common of all. It exhibits moderate instability and moderate to severe pain as well as swelling.
- Third degree – Most severe of all. Ligament gets completely ruptured. Joint is unstable and condition is marked by severe pain and swelling.
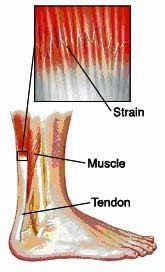 On the other hand, strains are injury pertaining to tendons or the muscles. Tendons are connective tissues by which muscles are attached to joints. Stains can occur during running or jumping as they include a sudden stretching and contracting motion. The symptoms of sprains are similar to that of a sprain which includes pain, swelling, stiffness and reduced capability of function. A strain is also known as “torn muscle”, “ruptured tendon” and “muscle pull”. Like sprains, strains are also categorised according to their severity.
On the other hand, strains are injury pertaining to tendons or the muscles. Tendons are connective tissues by which muscles are attached to joints. Stains can occur during running or jumping as they include a sudden stretching and contracting motion. The symptoms of sprains are similar to that of a sprain which includes pain, swelling, stiffness and reduced capability of function. A strain is also known as “torn muscle”, “ruptured tendon” and “muscle pull”. Like sprains, strains are also categorised according to their severity.
- First Degree – Mildest of all marked by little tissue tearing and little pain. Still no effect on motion
- Second Degree – marked by torn muscle or tendon tissues. Limited motion
- Third Degree – Most severe of all and marked by limited or no movement. It may also show no pain after the initial injury. Immediate treatments for both include rest, icepacks, compression and elevation which are called as RICE.
Generally, most of the sprains and strains do not require any serious treatment as they get to resolve with time. However, sometimes physical therapy or surgery may be required. Anti-inflammatory medications are also prescribed for getting relief from pain and inflammation of the injury.
Comparison between Sprain and Strain:
|
|
Sprain |
Strain |
|
Definition |
An injury (stretch or tear) affecting a ligament |
An injury (stretch or tear) effecting the muscle itself or a tendon |
|
Common location |
Ankle |
Lower back and in the hamstring muscle in the back of thigh |
|
Common signs |
Pain, bruising, swelling, and inflammation |
Pain, muscle spasm, muscle weakness, swelling, inflammation, and cramping |
|
Causes |
Caused by trauma — a fall, twist, or blow to the body |
Acute strains are caused due to stretching or pulling a muscle or tendon. Chronic strains are due to overuse of muscles and tendons. |
Images Courtesy: nzihf.co.nz









Add new comment