Difference between Measles and Chickenpox
Key Difference: Measles is a respiratory disease that is caused by Paramyxovirus virus from the Morbillivirus genus. Chickenpox is one of the most common diseases that children acquire and is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV).
Measles and Chickenpox are most common types of diseases that a person undergoes when they are a child. These diseases are becoming uncommon due to the widespread use of successful vaccines for these illnesses. Though, both the diseases cause rashes in the form of red spots, they are different from each other.
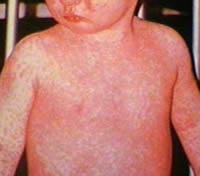 Measles is a respiratory disease that is caused by Paramyxovirus virus from the Morbillivirus genus. Measles, also known as English measles, morbilli or rubeola, is a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA viruses. It is an airborne disease that is spread through respiration or contact with fluids from the infected person. The initial symptoms of measles occur within 10-12 days after a person is exposed to the infection after which in a few days the rash starts occurring. Measles can last from 10-21 days.
Measles is a respiratory disease that is caused by Paramyxovirus virus from the Morbillivirus genus. Measles, also known as English measles, morbilli or rubeola, is a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA viruses. It is an airborne disease that is spread through respiration or contact with fluids from the infected person. The initial symptoms of measles occur within 10-12 days after a person is exposed to the infection after which in a few days the rash starts occurring. Measles can last from 10-21 days.
Most common symptoms of measles include blotchy rash, fever, cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis (red, watery eyes), malaise (feeling run down, achy) and Koplik’s spots (tiny white spots with bluish-white centers found inside the mouth). This disease can create complication in children (especially with immunodeficiency due to other diseases), malnutrition and pregnant women. Measles is a curable disease and a vaccine is available for it. In many countries, most babies are administered the vaccine when they are born. In order to elevate the fever, non-aspirin based medications should be provided.

Chickenpox is one of the most common diseases that children acquire and is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV). Similar to measles, chickenpox is also an airborne disease that is easily spread by coughing, sneezing or coming in touch with infected person. The term chickenpox is believed to originate from the rash resembling chicken pecks. This virus takes about two days to manifest, usually with the rash, which then turns into itchy, raw pockmarks. The pockmarks (lesions) are contagious and remain so until they are crusted over, which approximately takes around six to eight days.
Most common symptoms of chickenpox are high fever, tiredness, loss of appetite, headache and rashes. The rash begins as small red dots on the face, scalp, torso, upper arms and legs, which then progresses into small bumps, blisters and pustules. Infants, adolescents and pregnant women (not immune to chickenpox) have a high risk for complications. Women that are immune to chickenpox, or have already encountered chickenpox produce antibodies that keep the fetus from getting infected. Vaccine for chickenpox is available and should be administered in two doses for children, adolescents and adults.
|
|
Measles |
Chickenpox |
|
Virus |
Paramyxovirus |
Varicella zoster virus (VZV) |
|
Spreading |
An airborne disease; can spread through respiration or contact with fluids from the infected person |
An airborne disease; can easily be spread by coughing, sneezing or coming in touch with infected person |
|
Other names |
English measles, morbilli, rubeola |
Varicella |
|
Symptoms |
Blotchy rash, fever, cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis (red, watery eyes), malaise (feeling run down, achy) and Koplik’s spots (tiny white spots with bluish-white centers found inside the mouth) |
high fever, tiredness, loss of appetite, headache and rashes |
|
Diagnosis |
Clinical diagnosis requires the patient to have a fever for at least 3 days, with one of the three C's (cough, coryza, conjunctivitis). Also can be diagnosed visibility of Koplik's spots |
The diagnosis of varicella is done with typical early "prodromal" symptoms, and then the characteristic rash |
|
Prevention |
The best prevention is to get the vaccine |
The best prevention is to get the vaccine |
|
Vaccine |
Vaccine is available; MMR vaccine is a combination of (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine |
Vaccine is available; CDC recommends two doses of chickenpox vaccine for children, adolescents, and adults; to reduce fever use non- aspirin based medication |
|
Complications |
Pneumonia, ear infections, diarrhea, blindness or encephalitis. |
Dehydration, pneumonia, bleeding problems, encephalitis, cerebellar ataxia, bacterial infections, blood stream infections, toxic shock syndrome, bone infections or joint infections |
Image Courtesy: medicalook.com, sheknows.com








Comments
Anonymous
Wed, 12/23/2015 - 04:48
good work
pramod baranwal
Mon, 04/07/2014 - 21:59
Add new comment