Difference between Keto and Low Carb Diet
Key Difference: Keto Diet works by limiting carbohydrate intake and putting your body in the state of Ketosis, where it burns fat instead of carbs to produce energy. A low carb diet is any diet that simply limits the carb intake. Keto is a type of low carb diet, but there are also other diets that can be low carb diet such as Atkins, Paleo, etc.
 Diets have become extremely popular especially with a lot of celebrities endorsing a diet or two, swearing how it changed their lives. However, with the number of different diets that are currently on the market, understanding which diet is which can definitely become confusing. It also doesn’t help that a lot of diets have variations within themselves. In this article, we’ll take a look at how keto diets differ from low carb diets.
Diets have become extremely popular especially with a lot of celebrities endorsing a diet or two, swearing how it changed their lives. However, with the number of different diets that are currently on the market, understanding which diet is which can definitely become confusing. It also doesn’t help that a lot of diets have variations within themselves. In this article, we’ll take a look at how keto diets differ from low carb diets.
Keto diet, short for Ketogenic Diet, is a type of diet that focuses on reducing the intake of carbohydrates in the body to push it into a state of ketosis. The Ketosis state is when the body, which usually converts carbs into glucose in order to create energy, turns to burning fat instead. The diet works by reducing carb intake and increasing fat and protein in the diet. The suggested diet is 25% protein, 5% carbs and 70% fat, which helps push the body in the state of ketosis.
Although now the Keto diet is used as a weight loss mechanism, it was originally actually built as a way to reduce seizures in patients. Research showed limit carbs showed positive results in reducing the amount of seizures. However, it also cause weight loss in the patient. So, it was also suggested for cases where extreme weight loss is required. Keto has since included multiple variations.
On the other hand, low carb diets is actually an umbrella term. It includes Keto and other diets that restrict carbohydrates in daily intake. While, Keto diet is a type of low carb diet, not all low-carb diets are Keto. Other low carb diets include different percentages and generally allow a slightly higher percentage of carbohydrates compared to Keto. Low carb diets work by putting the body into short periods of ketosis, helping body lose weight.
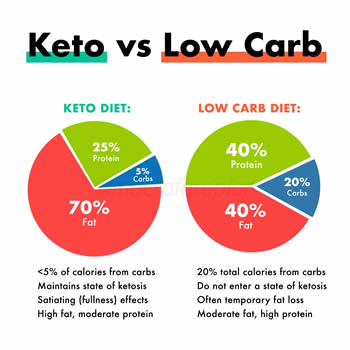 Most low carb diets are aimed at losing weight and hence include a lower fat percentage and a slightly higher carb allowance. The most common approximate division includes 40% protein, 20% carbohydrates and 40% fat. However, if not done right low carb diets can hinder the body instead of helping it. It can spike your blood sugar and drop your energy levels if your body does not go into the state of ketosis. Low carb diets are also often designed to be either short term or long-term depending on the type of results a person is looking for.
Most low carb diets are aimed at losing weight and hence include a lower fat percentage and a slightly higher carb allowance. The most common approximate division includes 40% protein, 20% carbohydrates and 40% fat. However, if not done right low carb diets can hinder the body instead of helping it. It can spike your blood sugar and drop your energy levels if your body does not go into the state of ketosis. Low carb diets are also often designed to be either short term or long-term depending on the type of results a person is looking for.
Diets can often be complicated and simply jumping onto a bandwagon is not a great idea. Each diet differs depending on the person’s height, weight, body type, routine, and their metabolism. So before you jump on any diet, it is important to discuss how the diet can affect your body with a doctor or a nutritionist. They can help better guide you on if you should be following the diet or if another diet may be right for you.
Comparison between Keto and Low Carb Diet:
|
|
Keto Diet |
Low Carb Diet |
|
Full Name |
Ketogenic Diet |
Includes multiple diets – including Keto, Atkins, Paleo, etc. |
|
Definition |
Pushing your body into a state of Ketosis, where the body uses fat for fuel |
Randomly eating fewer carbohydrates |
|
Developed By |
Although, the Keto diet has been in debate around 1911s, Russell Morse Wilder is credited with coining the term, “Ketogenic Diet” |
No singular record as it includes multiple diets |
|
Developed In |
1921 |
Records show similar diets as early as 1700s |
|
Objective of Diet |
Limit carbohydrate intake including some fruits and vegetables |
Limit high carbohydrate foods including some fruits and vegetables |
|
Purpose |
Originally to help reduce epileptic seizures Commonly, to help reduce weight |
To help reduce weight |
|
% of Protein |
Approx. 25% |
Approx. 40% |
|
% of Carbs |
Approx. 5% |
Approx. 20% |
|
% of Fat |
Approx. 70% |
Approx. 40% |
|
Phases |
Maintain same diet through the entire dieting process |
Diet fluctuates depending on the type of diet you are following |
|
Body Status |
During the entire diet, your body must be ketosis for the diet to work |
Ketosis only accounts for a short period, the rest of time the body is not in ketosis |
|
Easier to Follow |
Harder to follow since you have to measure carb, protein and fat. |
Easier to follow as you have the option for adapting according to your needs |
|
Sustainability |
Shorter |
Longer |
|
Safety |
Less safe as it limits carbs throughout the entire diet and maybe lifetime |
Can cause irritability as sugar levels spike. Can also reduce energy when sugar levels drop |
References: Wikipedia (Keto, Low-carb), Ample Meal, Dr. Anthony Gustin, Ruled.Me, Low Carb Yum, Lakanto, Dr. Jockers Image Courtesy: popspizzaandpasta.com, macrofare.com








Add new comment