Difference between Water and Heavy Water
Key Difference: Water is a composed chemical that is essential for almost every life form. A water molecule is formed by the combination of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. Heavy water is also water but with an exception; it contains more than the normal proportion of the hydrogen isotope deuterium.
.jpg) Water is a chemical compound that is essential for almost every life form. A water molecule is formed by the combination of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. Therefore, it is also symbolized as H2O. It is quiet interesting to know that a single drop of water contains billions of water molecules. In its pure form it is colorless, odorless and tasteless. It is a unique substance, as it is the only substance that is found naturally in all three states (solid, liquid and gas). It is also regarded as the “universal solvent”. It freezes at 32° Fahrenheit (F) (0° Celcius) and boils at 212° F (100° C). Water has a high specific heat index and surface tension.
Water is a chemical compound that is essential for almost every life form. A water molecule is formed by the combination of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. Therefore, it is also symbolized as H2O. It is quiet interesting to know that a single drop of water contains billions of water molecules. In its pure form it is colorless, odorless and tasteless. It is a unique substance, as it is the only substance that is found naturally in all three states (solid, liquid and gas). It is also regarded as the “universal solvent”. It freezes at 32° Fahrenheit (F) (0° Celcius) and boils at 212° F (100° C). Water has a high specific heat index and surface tension.
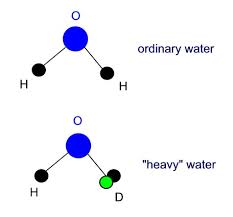 Heavy water (Deuterium Oxide) is also water, but it contains more than the normal proportion of the hydrogen isotope - deuterium (2H, rather than 1H). It greatly differs from water in terms of its density. Heavy water is 11 percent denser than ordinary water. Heavy water may be any of the deuterium oxide, D2O or deuterium protium oxide and DHO. Like water, heavy water also occurs naturally. However, it is not that common as water. Due to the isotopic substitution with deuterioum, the bond energy of the water’s hydrogen-oxygen bond gets affected. This is basically responsible for bringing the changes in various physical and chemical properties of heavy water.
Heavy water (Deuterium Oxide) is also water, but it contains more than the normal proportion of the hydrogen isotope - deuterium (2H, rather than 1H). It greatly differs from water in terms of its density. Heavy water is 11 percent denser than ordinary water. Heavy water may be any of the deuterium oxide, D2O or deuterium protium oxide and DHO. Like water, heavy water also occurs naturally. However, it is not that common as water. Due to the isotopic substitution with deuterioum, the bond energy of the water’s hydrogen-oxygen bond gets affected. This is basically responsible for bringing the changes in various physical and chemical properties of heavy water.
Comparison between Water and Heavy Water:
|
|
Water |
Heavy Water |
|
Definition |
Water is a chemical compound that is essential for almost every life form. A water molecule is formed by the combination of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. |
Heavy water is water but with an exception; it contains more than normal proportion of the hydrogen isotope deuterium. |
|
Density |
Less |
11 percent more than the water |
|
Boiling point |
100° C |
101.4 °C |
|
Freezing point |
0° C |
3.8° C. |
|
PH Value |
Comparatively low |
Comparatively high |
|
Viscosity, heat of vaporization, refractive index |
Comparatively low |
Comparatively high |
|
Shape |
Broader structure |
Tetrahedral shape |
|
Ice |
Floats on the surface of water |
Ice made from heavy water sinks |
|
Chemical reactions |
Comparatively fast |
Comparatively slow |
|
Uses |
|
|
Image Courtesy: h2obuildingservices.co.uk, lpl.arizona.edu









Comments
Peter
Thu, 12/29/2016 - 11:34
Thanks, Peter. It has been fixed now.
dbadmin
Thu, 12/29/2016 - 11:39
Nicholas
Fri, 01/08/2016 - 07:19
Add new comment