Difference between Clipping and Culling
Key Difference: Clipping is the process where software is programmed to identify and remove a portion of a picture which is either inside or outside the viewing frame. Occlusion culling (OC) is the process in which software is used to determine the surfaces and parts of the image that is not visible to the user, because it lies behind another object or surface.
Clipping and culling are terms that are commonly found in computer graphics when designing video games. These are techniques that are used when creating video games by programmers and designers. Both these techniques are similar and are also used for similar purposes; they are often confused by people who are not into the field. These two techniques have various differences between them.
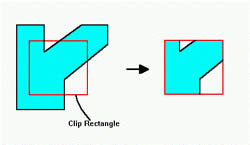 Clipping is the process where software is programmed to identify and remove a portion of a picture which is either inside or outside the viewing frame. The region which is clipped is outside the viewing frame or the clipping window. This is done in graphics or games in order to eliminate the portions of the game or images that will not be visible to the player. This saves time and increases the rendering rate for the graphics. For example, a user editing 2D graphics zooms in and only the top half of the image is viewed, clipping enables the computer to not waste time loading the bottom half of the image which speeds up loading of the image.
Clipping is the process where software is programmed to identify and remove a portion of a picture which is either inside or outside the viewing frame. The region which is clipped is outside the viewing frame or the clipping window. This is done in graphics or games in order to eliminate the portions of the game or images that will not be visible to the player. This saves time and increases the rendering rate for the graphics. For example, a user editing 2D graphics zooms in and only the top half of the image is viewed, clipping enables the computer to not waste time loading the bottom half of the image which speeds up loading of the image.
In 3D images, clipping is used in a different manner. Now if a 3-D model of a town is created, however, the camera can only view the town from a certain angle or a certain degree, anything which is out of the field of view, the computer does not alter, shade or add details, or even render the back image altogether. It can also be used to not add texture or details to objects that are far away from the camera. The algorithm lets the rendering code skip the details and enables the program to run faster, this is a prominent method used when designing graphics for cell phones.
Clipping plays an important part during developing video games and should be used carefully in order to maximize the frame rate and visual quality of the game. Each game developer is assigned a certain ‘budget’ of polygons that can be drawn in each video frame, as it is expensive to transform, texture, and shade a polygon. Hence by clipping, the developer can increase the budget and also maximize the game’s visual quality. Clipping technique is used commonly when objects are partially visible and is done just before rasterization. Clipping is done by the graphics system.
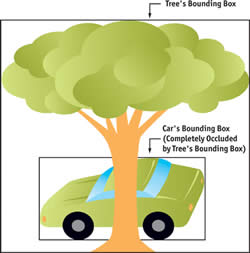
Occlusion culling (OC) is the process in which software is used to determine the surfaces and parts of the image that is not visible to the user, because it lies behind another object or surface. Culling is also known as hidden surface removal (HSR), occlusion culling (OC) or visible surface determination (VSD). A hidden surface determination algorithm is used in order to find objects that are not visible to the player or the viewer as it lies behind another object and these objects are not rendered on the screen. For example, part of a car is visible, but the rest of the car is hidden behind a building. The rest of the car, which should not be visible to the user, even in the real world, as it lies behind the building is prevented from being rendered by the machine.
This process plays an important role as it allows the computer to keep its speed by removing unnecessary objects that won’t be visible to the viewer. A good example of seeing culling is, when playing a game, certain objects are only show partially or are hidden, however when the players goes to view the particular object, the user mostly gets a black image or it just zooms to that particular image. Culling is popular method that speeds up the rendering of large scenes that have a moderate to high depth complexity. Culling can also be done for faces that may be in the background scenes and not visible, this allows the program to remove the details and or refrain from drawing the face completely in order to save memory.
Various different types of occlusion culling approaches include potentially visible set or PVS rendering, where scenes are divided into sections and visibility is pre-computed for the scene; portal rendering divides a scene into cells, sectors or portals and then removes the images that are not visible. There are two different types of culling such as MCCAM Cull operation and Subpixel Cull operation. Culling is done before transformation and lighting of a scene.
Image Courtesy: cc.gatech.edu, http.developer.nvidia.com









Add new comment