Difference between Windows 7 and Windows 8
Key Difference: Windows 7 and Windows 8 are two different operating systems that are offered by Microsoft. Windows 7 was offered as an upgrade to the Windows Vista, while Windows 8 was launched to make the system uniform on tablets, PCs and laptops. Windows 8 offers a new Live Tile Start Menu that is similar to the ones available on Windows phones.
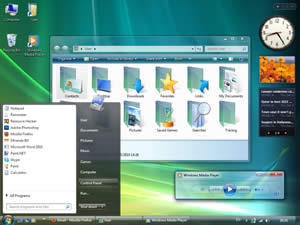 Windows 7 and Windows 8 are two different types of operating systems that are available on Microsoft PCs, notebooks and tablets. The company has been constant launching new operating systems in order to adapt to the new technology or make it device more user-friendly. Windows 7 was launched as an upgrade to the Windows Vista, while Windows 8 is set to replace Windows 7 in the coming years.
Windows 7 and Windows 8 are two different types of operating systems that are available on Microsoft PCs, notebooks and tablets. The company has been constant launching new operating systems in order to adapt to the new technology or make it device more user-friendly. Windows 7 was launched as an upgrade to the Windows Vista, while Windows 8 is set to replace Windows 7 in the coming years.
Windows 7 was launched in October 2009 as a way to make the computer more user-friendly, as well as offer some upgrades on the already present Windows Vista system. While, Vista sought to offer many new features, Windows 7 was launched as an upgrade that was designed to work with Vista-compatible applications and hardware. The main change that was offered with Windows 7 was the new Taskbar that was dubbed as ‘Superbar’. The main reason for the launch of Windows 7 was to make a more user-friendly windows system and incorporate the new features of Windows Vista that were appealing to the people, but failed when Vista tanked.
The new features that were introduced on Windows 7 included: extended support for Vista themes, gadgets side bar that allowed users to add calendar, clock and other such gadgets on the desktop, Windows Explorer supports Libraries (which shows all virtual folders and content in a unified view), changes to the Start Menu, shut down button has been altered with more options only available if the arrow is clicked, jump lists on the taskbar when hovered on right-clicked on, search box has been extended to support items in Control Panel. Additional features include Aero Snap and Aero Shake. When Windows is dragged to the top right hand side of the screen it automatically maximized and minimizes when it is pulled away. In Aero Shake, shaking a window on the screen will only keep the shaken window active and the rest of windows will minimize. Additional keyboard shortcuts have been introduced.
Diffen.com lists the shortcuts as:
- Win+Space operates as a keyboard shortcut for Aero Peek.
- Win+Up and Win+Down are new shortcuts for Maximize and Restore/Minimize.
- Win+Shift+Up vertically maximises the current window
- Win+Left and Win+Right snap the current window to the left or right half of the current display; successive keypresses will move the window to other monitors in a multi-monitor configuration.
- Win+Shift+Left and Win+Shift+Right move the current window to the left or right display.
- Win+ + and Win+ - (minus sign) zoom the desktop in and out.
- Win+Home operates as a keyboard shortcut for Aero Shake.
- Win+P shows an "external display options" selector that gives the user the choice of showing the desktop on only the computer's screen, only the external display, on both at the same time (mirroring), or on both displays with independent desktops (extending).
- Shift + Click, or Middle click starts a new instance of the application, regardless of whether it's already running.
- Ctrl + Shift + Click starts a new instance with Administrator privileges; by default, a User Account Control prompt will be displayed.
- Shift + Right-click shows the classic Window menu (Restore / Minimize / Move / etc); right-clicking on the application's thumbnail image will also show this menu. If the icon being clicked on is a grouped icon, the classic menu with Restore All / Minimize All / Close All menu is shown.
- Ctrl + Click on a grouped icon cycles between the windows (or tabs) in the group.
Windows 7 was launched in six different editions: Home Premium Edition, Professional Edition, Ultimate Edition, Starter Edition, Enterprise Edition and Home Basic Edition. The first three editions were available for retail sale for consumers, while the Starter edition was preinstalled by OEM, the Enterprise edition only by volume licensing, and Home Basic only to certain developing countries' markets.The Windows 7 was a hit with many of the Microsoft customers and was used widely as an operating system. The Windows 7 required a 1 GHz processor, 1 GB RAM, DirectX 9 graphics processor with WDDM driver model 1.0, 16-20 GB (depending on architecture) free disk space and a DVD-ROM drive.
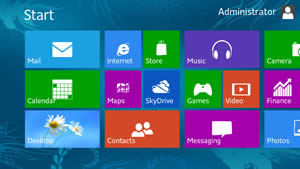 Windows 8 is the latest operating system by Microsoft for its PCs, laptops and tablets. The newest OS hit the markets in October 2012 and had a whole new look. The company has launched the operating system keeping in mind the constant upgrade from keyboard and mouse PCs to touch tablets. Windows 8 was launched with touch compatibility in mind. The system sports a whole new Menu Screen, with a new ‘Live Tile’ format that is found in the Windows phones. These tiles automatically update to show users new e-mails or other information.
Windows 8 is the latest operating system by Microsoft for its PCs, laptops and tablets. The newest OS hit the markets in October 2012 and had a whole new look. The company has launched the operating system keeping in mind the constant upgrade from keyboard and mouse PCs to touch tablets. Windows 8 was launched with touch compatibility in mind. The system sports a whole new Menu Screen, with a new ‘Live Tile’ format that is found in the Windows phones. These tiles automatically update to show users new e-mails or other information.
Windows 8 also supports new advancing technology such as USB 3.0, 4Kn Advanced Format, near field communications, cloud computing, and the low-power ARM architecture. This is the first OS that allows ARM architecture support, with the previous OS only supporting IA-32 and x86-64 architectures. It also offers built-in antivirus capabilities and advanced security features. Other features that make this OS handier are the Windows Store and app compatibility. The OS supports apps and are allow certain apps to dock on one side of the screen, while other apps can open in to proper programs. The OS also allows users to purchase and download apps from the Windows Store and use them on their laptops, PC as they would on their smartphones.
Windows 8 is offered in four editions: Windows 8, Windows 8 Pro, Windows 8 Enterprise and Windows RT. Windows 8 comes pre-loaded on the new PCs by the company. Windows 8 Pro is aimed at power users and professionals. Windows 8 Enterprise is aimed at business environments and is available through volume licensing, while Windows RT is the only edition comes preloaded on new ARM-based devices for Windows. In order to run Windows 8, the user must have certain system requirements: 1 GHz clock rate, 1-2 GB RAM (depending on the architecture), DirectX 9 graphics device WDDM 1.0 or higher driver, 1024×768 pixels display, keyboard and mouse and 16-20 GB internal storage space.
|
|
Windows 7 |
Windows 8 |
|
License |
Proprietary commercial software |
Proprietary commercial software |
|
Worldwide release |
October 22, 2009 |
October 26, 2012 |
|
Stable release |
February 22, 2011 |
August 1, 2012 |
|
Kernel type |
Hybrid |
Hybrid |
|
Platform support |
IA-32 and x86-64 |
IA-32, x64, and ARM |
|
Preceded by |
Windows Vista |
Windows 7 |
|
Succeeded by |
Windows 8 |
- |
|
Physical Memory Limits |
2 – 192 GB depending on the version and architecture. |
4 GB -2048 GB depending on architecture. |
|
Processors |
32 for 32-bit, 256 for 64-bit |
32 for 32-bit, 256 for 64-bit |
|
New Features |
|
|
|
Removed Features |
|
|
Image Courtesy: fediafedia.deviantart.com, pcadvisor.co.uk









Add new comment