Difference between HashMap and HashTable
Key Difference: In computer science, a hashTable or a hashMap refers to a data structure that links keys (names) with values (attributes). In Java, there are some important differences between the two like: HashTable is synchronized and HashMap is unsynchronized. A HashTable does not allow null keys. However, a HashMap allows a single null key and any number of null values.
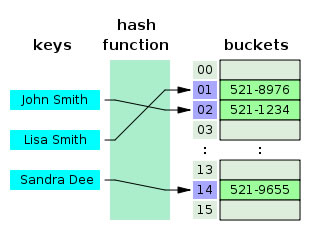
HashMap and hashTable are data structures that are parts of the Java collection. They use key-value pairs in order to store objects. They both share some similarities, such as both implement java.util.Map interface and both work on the principle of hashing. However, when we refer to them in context to the Java programming language, there are numerous differences between the two.
A hashTable is used to store and retrieve a value by using a key. For this purpose, the key must be unique. The table that is used to store the key and value pairs is known as a hash table. A hash table is formed by using an algorithm that hashes the keys. This hash function is used to assign numbers to the input data, and then the data is stored as the array index which corresponds to the calculated or evaluated number.
 Like a hashTable, a hashMap also works on the same principles of hashing. It can be considered as a hash table based implementation of the Map interface. However, it differs from the hashTable on few points. HashMap is unsynchronized, whereas hashTable is synchronized. Synchronization means that at a particle time, only one thread is able to modify the table. Thus, to perform an update operation on the hashTable, a lock must be acquired on the table. For that particular time, the other threads have to wait. After the unlocking, the other threads may proceed and work on the table. Another major difference between the two is that hashTable does not allow a null key. However, hashMap allows a single null key and any number of null values.
Like a hashTable, a hashMap also works on the same principles of hashing. It can be considered as a hash table based implementation of the Map interface. However, it differs from the hashTable on few points. HashMap is unsynchronized, whereas hashTable is synchronized. Synchronization means that at a particle time, only one thread is able to modify the table. Thus, to perform an update operation on the hashTable, a lock must be acquired on the table. For that particular time, the other threads have to wait. After the unlocking, the other threads may proceed and work on the table. Another major difference between the two is that hashTable does not allow a null key. However, hashMap allows a single null key and any number of null values.
Comparison between HashMap and HashTable:
|
|
HashMap |
HashTable |
|
Synchronization |
It is non synchronized |
It is synchronized (thread safe) |
|
Null Values |
It permits null values as key and value |
It does not permit nulls |
|
Introduction in java |
Java version 1.2 |
First version of java development kit |
|
Performance |
Comparatively better |
Comparatively poor |
|
Extends |
It extends AbstractMap class |
It extends Dictionary class which is quite old |
|
Iteration of keys |
Iterator is used for iterating the keys |
Enumeration interface is used for iterating keys |
|
Applications |
Better for non-threaded applications |
Generally, safe for multithreaded applications |
|
Serialization |
Not serialized |
Serialized |
|
Alternative |
One can use concurrent hashMap for multi-thread environment |
No such alternative |
Image Courtesy: wikipedia.org, way2java.com









Add new comment