Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis
Key difference: Mitosis is the process through which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets. Essentially, a cell (the mother cell) divides itself into two cells (the daughter cells), which are identical to the mother cell. Meiosis, on the other hands, is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. In the process of meiosis, a cell that contains two copies of each chromosome, one from the mother and one from the father (the zygote – which is a female egg fertilized by male sperm), produces four cells containing one copy of each chromosome.
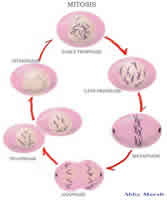 All cells include a process called cell division in their life cycle. Cell division accounts for approximately 10% of the cell cycle. It is a process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. There are three main types of cell division processes: binary fission, mitosis and meiosis.
All cells include a process called cell division in their life cycle. Cell division accounts for approximately 10% of the cell cycle. It is a process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. There are three main types of cell division processes: binary fission, mitosis and meiosis.
Binary fission takes place in prokaryotes, single-celled organisms that lack a cell nucleus. Eukaryotes, organisms whose cells contain complex structures within their membranes, experience either mitosis or meiosis. All of these processes are a method of reproduction and DNA replication.
Mitosis is the process through which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets. These are called the daughter cells. Essentially, a cell (the mother cell) divides itself into two cells (the daughter cells), which are identical to the mother cell. This is done by dividing the nucleus of the original cell into two parts. These daughter cells contain the same number of chromosomes as the mother cell.
Mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction. This allows an organism to clone exact copies of the original cell. This method of reproduction is rapid and effective. However, as the offspring are identical to the mother, there is no mechanism for introducing diversity.
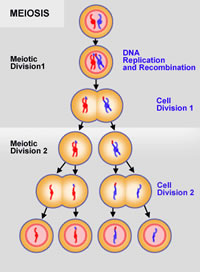
Meiosis, on the other hands, is a type of sexual reproduction. It is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. Gametes are the sperm and egg cells in most organisms, such as all animals and land plants.
In the process of meiosis, a cell that contains two copies of each chromosome, one from the mother and one from the father (the zygote – which is a female egg fertilized by male sperm), produces four cells containing one copy of each chromosome. The resulting chromosome is a unique mixture of maternal and paternal DNA. This allows the offspring to be genetically distinct from either parent. Meiosis introduces genetic diversity within the population.
Meiosis differs from mitosis in two important aspects. Meiosis produces four offspring cells with half of the original cells’ chromosomes, whereas mitosis produced two offspring cells with identical chromosomes as the original cell. Furthermore, meiosis allows for genetic diversity by allowing the mixing of chromosomes, whereas mitosis does not.
A comparison between mitosis and meiosis:
|
|
Mitosis |
Meiosis |
|
Description |
Mitosis is a process of asexual reproduction in which the cell divides in two producing a replica, with an equal number of chromosomes in haploid cell |
Meiosis is a type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell. |
|
Type of reproduction |
Asexual |
Sexual |
|
Function |
Cellular reproduction and general growth and repair of the body |
Sexual reproduction |
|
Takes place in |
All organisms |
Humans, animals, plants, fungi |
|
Types of cells |
Within somatic cells (cells that make up the body) |
Takes place within gamete cells (sex cells). |
|
Number of divisions |
Mitosis undergoes only one division. |
Meiosis undergoes two divisions. |
|
Produces |
Two identical daughter cells |
Four meiotic products or haploid gametes |
|
Mixing of chromosomes |
Mixing of chromosomes cannot occur. |
Mixing of chromosomes can occur. |
|
Number of chromosomes |
Same as parent cell |
Half of the original gamete cell before meiosis. |
Image Courtesy: med.mui.ac.ir, dbscience3.wikispaces.com









Comments
Good info
D4n
Tue, 01/27/2015 - 22:39
great information
yo yo
Thu, 03/20/2014 - 00:15
Chanks Guys!!
Erin Grace
Wed, 02/05/2014 - 12:40
good info
viviansandra
Sat, 02/01/2014 - 21:17
Add new comment