Difference between RSTP and PVST
Key difference: The Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) provides a significantly faster spanning tree convergence after a topology change as compared to the original STP. In order to do this, RSTP provides new introduces new convergence behaviors and bridge port roles. PVST stands for Per-VLAN Spanning Tree. It is Cisco's proprietary version of the Spanning Tree Protocol. PVST allows for the creation of a spanning tree for each VLAN.
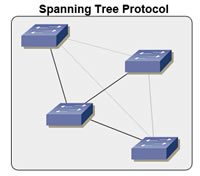 RSTP and PVST are types of the spanning tree protocol. The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol is essentially used for any bridged Ethernet local area network (LAN). The STP ensures a loop-free topology in the Ethernet LAN. It does so by preventing bridge loops and broadcasting the radiation that results from them.
RSTP and PVST are types of the spanning tree protocol. The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol is essentially used for any bridged Ethernet local area network (LAN). The STP ensures a loop-free topology in the Ethernet LAN. It does so by preventing bridge loops and broadcasting the radiation that results from them.
The STP is standardized as IEEE 802.1D. STP creates a spanning tree within a mesh network of connected layer-2 bridges. Typically, the layer-2 bridges are Ethernet switches. The STP disables those links that are not part of the spanning tree and leaves a single active path between any two network nodes.
The STP also allows a network design to include spare and/or redundant links. These provide automatic backup paths in case an active link fails. These spare links are included without the danger of bridge loops, or the need for manual enabling/disabling of the backup links.
The Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) was introduced in 2001 as 802.1w by the IEEE. RSTP provides a significantly faster spanning tree convergence after a topology change as compared to the original STP. STP can take 30 to 50 seconds to respond to a topology change, however, RSTP can do this is 3 times 2 seconds default or within a few milliseconds of a physical link failure.
In order to do this, RSTP provides new introduces new convergence behaviors and bridge port roles. STP's original number of states a port can be was five, however, RSTP reduces this to three.
RSTP was designed to be backwards-compatible with standard STP. However, the Standard IEEE 802.1D-2004 incorporates RSTP and obsoletes the original STP standard.

PVST stands for Per-VLAN Spanning Tree. It is Cisco's proprietary version of the Spanning Tree Protocol. In an Ethernet switched environment there are multiple Virtual LANs. Hence, it is often necessary to create multiple spanning trees. This is done so that the traffic from different VLANs uses different links. PVST does that. It allows for the creation of a spanning tree for each VLAN.
As Cisco's proprietary version of the Spanning Tree Protocol, they cannot be used on most third party switches. Another such Cisco's protocol is the PVST+ (Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus). PVST works only with ISL, which is Cisco's proprietary protocol for VLAN encapsulation. This is due to the ISL’s embedded Spanning tree ID, which is the default protocol on Cisco switches that support ISL.
Due to the high penetration of the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN trunking standard and PVST's dependence on ISL, Cisco defined a different PVST+ standard. The PVST+ standard is compatible with 802.1Q encapsulation. This eventually became the default protocol for Cisco switches when Cisco discontinued and removed ISL support from its switches.
Image Courtesy: networkingtips-tricks.blogspot.com, cisco.com








Comments
venkateswarlu
Sun, 12/13/2015 - 21:38
Great explanation in simple words. Excellent !
Vinayak
Tue, 06/17/2014 - 17:13
Some things I had trouble understanding because of grammar problems.
P
Fri, 05/30/2014 - 20:48
Add new comment