Difference between Xylem and Phloem
Key difference: Xylem is responsible for transporting water and certain nutrients from the root to the rest of the plant. Phloem carries soluble organic material, i.e. food for the plant, which is produced in the leaves by photosynthesis to the other parts of the plant.
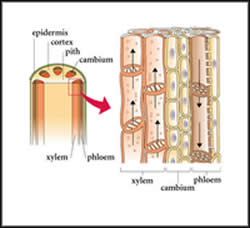 Xylem and phloem are the two types of vascular tissues that are present in plants. They are responsible for transporting water, minerals, food and other organic materials between the roots, stems and leaves of the plant. Xylem and phloem form vascular bundles with each other, which means that together they are responsible for the efficient transportation of food, nutrients, minerals, and water in the plant, and hence the survival of the plant.
Xylem and phloem are the two types of vascular tissues that are present in plants. They are responsible for transporting water, minerals, food and other organic materials between the roots, stems and leaves of the plant. Xylem and phloem form vascular bundles with each other, which means that together they are responsible for the efficient transportation of food, nutrients, minerals, and water in the plant, and hence the survival of the plant.
Xylem is a type of transport tissue in vascular plants that is responsible for transporting water and certain nutrients from the root to the rest of the plant. Thus, it essentially flows in one direction, that is, from the bottom up to the sky towards the top of the plant. Its main function is to effectively transport water and nutrients from the soil to the various parts of the plant. The word ‘xylem’ is derived from the Greek word ‘xylon’, meaning wood. This is because wood is the best-known xylem tissue which is found throughout the tree.
Xylem is a mixture of dead and living tissues, which are non-living at the time of maturity. It is made up of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, xylem fibres and ray parenchyma. Xylem cells are hard walled cells, which are stacked on top of each other and are mainly found in the center of the stem. Hence, xylem has another function, which is to provide mechanical support to the plant.
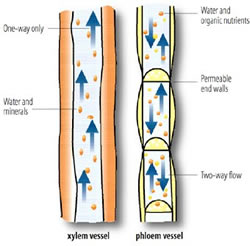
Xylem is surrounded by the phloem. Phloem is the other type of transport tissue in vascular plants. Its main function is to carry soluble organic material, i.e. food for the plant, which is produced in the leaves by photosynthesis to the other parts of the plant. This process is called translocation. To do this effectively it flows both up and down the stem, unlike the xylem, which only flows up.
The word ‘phloem’ is derived from the Greek word ‘phloos’, which means bark, as the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark in most trees. Phloem is made up of sieve cells, sieve tube elements, phloem parenchyma, phloem fibres, and phloem ray cells. It consists of both living and dead soft-walled cells, where the outer phloem is made up of dead cells and the inner phloem is made of living cells.
A detailed comparison between xylem and phloem:
|
|
Xylem |
Phloem |
|
Function |
Transportation of water and mineral from roots to other parts of the plant. Forms vascular bundles with phloem and gives mechanical strength to plant due to presence of lignified cells. |
Transportation of food and nutrients from leaves to storage organs and growing parts of plant. Forms vascular bundles with xylem. |
|
Takes place in |
Roots, stems and leaves |
Roots, stems and leaves |
|
Nature |
Non living tissue at maturity |
Living tissue |
|
Made up of |
Tracheids, vessel elements, xylemparenchyma, xylem sclerenchyma. |
Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, bast fibers, intermediary cells. |
|
Physical structure |
Tubular with hard walled cells |
Tubular with soft walled cells |
|
Movement |
Unidirectional – Moves up the plant's stem |
Bi-directional – Moves up or down the plant's stem |
Image Courtesy: plantmaterialsandusage.blogspot.in, icmag.com









Comments
nice to give knowledge
sri elton
Tue, 08/12/2014 - 20:03
i really like this
anshul suman
Fri, 08/08/2014 - 14:56
I like this
maryam
Sun, 05/04/2014 - 23:49
Add new comment