Difference between a Traditional and Roth IRA
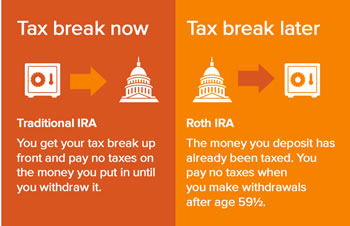
Key Difference: The primary difference between a Traditional IRA and a Roth IRA.is that in a Traditional IRA, any income put into the account is generally tax-free, ensuring that the person meets certain criteria. However, the income put into a Roth IRA is not tax free. Nevertheless, during the time of withdrawal these factors are reversed. Any money withdrawn from a Traditional IRA is taxable, whereas money withdrawn from a Roth IRA is generally tax free.
 Retirement planning is a something that should be started as soon as possible, however, that is easier said than done. This is made difficult sue to the fact most people do not even know of the products available out there for retirement planning, as well as the fact the rules and regular associated with them are quite confusing.
Retirement planning is a something that should be started as soon as possible, however, that is easier said than done. This is made difficult sue to the fact most people do not even know of the products available out there for retirement planning, as well as the fact the rules and regular associated with them are quite confusing.
One of the most popular plans out there for retirement savings is a 401K, second is an IRA. A 401K is only available for people who work for an employer who offers a 401K. Everyone else has no option but to sign up for an IRA. In fact, many people who have a 401K, still go ahead and sign up for an IRA in order to avail its many benefits. However, there are two different types of IRA accounts, a Traditional IRA and a Roth IRA.
The primary difference between a Traditional IRA and a Roth IRA.is that in a Traditional IRA, any income put into the account is generally tax-free, ensuring that the person meets certain criteria. However, the income put into a Roth IRA is not tax free. Nevertheless, during the time of withdrawal these factors are reversed. Any money withdrawn from a Traditional IRA is taxable, whereas money withdrawn from a Roth IRA is generally tax free.
 Another difference between the two is that anyone who is younger than 70½ can contribute to a Traditional IRA, whereas Roth IRAs don’t have age restrictions. Also anyone with earned income can contribute to Traditional IRAs, while Roth IRAs have income-eligibility restrictions, which means that only people who fit into certain categories of minimum and maximum income can contribute to a Roth IRA.
Another difference between the two is that anyone who is younger than 70½ can contribute to a Traditional IRA, whereas Roth IRAs don’t have age restrictions. Also anyone with earned income can contribute to Traditional IRAs, while Roth IRAs have income-eligibility restrictions, which means that only people who fit into certain categories of minimum and maximum income can contribute to a Roth IRA.
One more difference between the two is that when one reaches the age of 70½, they must start withdrawing the required minimum distributions (RMDs), mandatory, taxable withdrawals of a certain percentage of the funds, whether they need the money or not. A Roth IRA does not have any such restrictions, and the money can be left in the account to grow. In fact, one need not make any type of withdrawal during their lifetime.
Comparison between a Traditional and Roth IRA:
|
|
Traditional IRA |
Roth IRA |
|
Type |
Retirement Plan |
Retirement Plan |
|
Purpose |
Financial Planning |
Financial Planning |
|
Taxable |
May or may not be taxable depending on their tax bracket as well as other factors |
May or may not be taxable depending on their tax bracket as well as other factors |
|
Age |
Anyone who is younger than 70½ can contribute to a Traditional IRA |
Roth IRAs don’t have age restrictions |
|
Income |
Anyone with earned income can contribute |
Has income-eligibility restrictions. Only people earning about those limitations can contribute |
|
Taxes |
Contributions are tax deductible on both state and federal tax returns for the same year |
Contributions are not tax deductible, but earnings and withdrawals are generally tax-free. |
|
Withdrawals |
Traditional IRAs require one to start taking required minimum distributions (RMDs), mandatory, taxable withdrawals of a certain percentage of the funds, at age 70½, whether they need the money or not. |
No such restrictions |
Reference: Wikipedia (IRA, Traditional IRA, Roth IRA), RothIRA, Time, CNN Image Courtesy: nextgenerationtrust.com, voya.com









Add new comment