Difference between Bacteria and Algae
Key Difference: Bacteria (singular: bacterium) are single celled micro-organisms that belong to the group of Prokaryotics. Algae (singular: alga) are Eukaryotic organisms (unicellular or multi-cellular) that contain chlorophyll and carry out the process of photosynthesis.
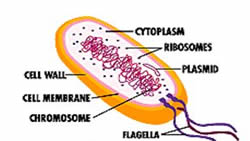 Bacteria are single celled micro-organisms that have a varied range of metabolic types, geometric shapes and environmental habitats. Their structure lack nucleus and customarily have no organelles. Most bacteria consist of a ring of DNA surrounded by cellular machinery, contained within a fatty membrane.
Bacteria are single celled micro-organisms that have a varied range of metabolic types, geometric shapes and environmental habitats. Their structure lack nucleus and customarily have no organelles. Most bacteria consist of a ring of DNA surrounded by cellular machinery, contained within a fatty membrane.
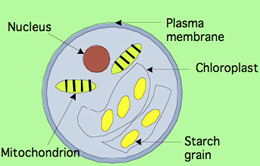
Algae are simple Eukaryotic photosynthetic autotrophs. They can be unicellular as well as multi-cellular. They belong to the kingdom Protista. Due to the presence of chlorophyll, Algae are capable of making their own food and the process is referred to as photosynthesis. Most of them are microscopic. However, few are quite large and can exceed in meters lengthwise. Green alga can easily be seen on the bark of trees.
Some of the characteristics of both are listed below in the table:-
|
|
Bacteria |
Algae |
|
Structure |
Most bacteria consist of a ring of DNA surrounded by cellular machinery, contained within a fatty membrane. |
Vegetative Structures of multicellular algae: Thallus: Body. Lacks conductive tissue. Holdfasts: Anchor alga to rock. Stipes: Hollow, stem-like structures. Does not support weight. Blades: Leaf-like structures. Pneumatocyst: Floating, gas-filled bladder |
|
Habitat |
Bacteria are found everywhere. They can survive and thrive in water, on skin, surfaces, carpet, earth, stone and especially dead flesh. |
Algae are found in water bodies, terrestrial environments and even in unusual environments such as snow and ice. |
|
Domain |
Prokaryote |
Eukaryote |
|
Cell walls |
Cell walls are make of peptidoglycan. |
Cell walls are composed of components such as cellulose, proteins, agar, carrageenan, silicates, algin, calcium carbonate. |
|
Nucleus |
Absent |
Present |
|
Size |
A few micrometers in length |
From microscopic to meters long |
|
Shape |
Come in three different possible shapes: Cocci = sphere shape Bacilli = rod shape Spirella = spiral shape |
Various shapes like elliptical and filamentous |
|
Usefulness |
Some are useful |
Most are beneficial |
|
Antibiotics |
Kill Bacteria |
Affect Algae |
|
Diseases Caused |
Cholera, tuberculosis, lyme disease, pertussus, salmonella, staph infections, strep throat, leprosy, tetanus, diptheria, E.coli, flesh eating (necrotizing fascitis) rickets, etc. |
Amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP), ciguatera fish poisoning (CFP), diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP), neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP), paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP), etc. |
|
Source of Energy |
Seize energy from the same essential sources as humans, including sugars, proteins, and fats. |
Most algae are able to make energy from sunlight, like plants do. |
|
Living |
Yes |
No |
|
How they are transmitted |
Direct contact with an infected person Contaminated food or water (Salmonella, E.coli) Dirty objects (tetanus) Infected animals (rabies) |
The toxins produced by the algae can enter the food chain through shellfish or fish. |
|
Reproduction |
Bacteria reproduce through binary fission, they split into two cells. |
Asexual reproduction (by cell division) and sexual reproduction (by producing pores) |
|
Motility |
Move through the environment using a structure known as the flagellum. |
Most algae are free floating and drift with water currents. |
|
Examples |
Lactobacillus, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, Bifidobacterium, Helicobacter pylori, Staphylococcus, etc. |
Brown, red and green Alga |
Image Courtesy: assignmentpoint.com, algaeindustrymagazine.com








Add new comment