Difference between CPU and Microprocessor
Key Difference: A CPU carries out all the arithmetic and computing functions of a computer, while a microprocessor houses the CPU, BIOS and memory access circuits.
Central Processing Units (CPUs) and microprocessors are common to people who often work with computing components; however for the rest of the public they often cause confusion. The terms microprocessor and CPU are often used to refer to the central processing unit, which is considered as the brain of the computer.
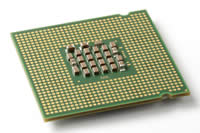 A central processing unit (CPU) is the hardware within a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. It is also called a central processor unit, or more commonly a processor. However, many mistakenly use the term CPU to refer to the housing unit that stores all of the computer’s hardware, whereas, in actuality it is just the small processor chip that runs the computer’s programs.
A central processing unit (CPU) is the hardware within a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. It is also called a central processor unit, or more commonly a processor. However, many mistakenly use the term CPU to refer to the housing unit that stores all of the computer’s hardware, whereas, in actuality it is just the small processor chip that runs the computer’s programs.
In large computers, the CPUs require one or more printed circuit boards. However, in personal computers and small workstations, the ones which most of us use, the CPU is housed in a single silicon chip called a microprocessor. The fundamental function of a CPU is to run or execute a program. A program is essentially a sequence of stored instructions, which is represented by a series of numbers that are kept in some kind of computer memory. CPUs follow a four step process in their operation: fetch, decode, execute, and writeback.
In addition to executing a program, the CPU is also responsible for keeping an eye over system functions, for executing scripts, and for making complex calculations, which are often used in software rendering. CPUs also initiate transfer of large blocks of data, as well as read or write data to and from peripheral devices, such as CDs, DVD, USB drives, etc. Since, the CPU is responsible for practically all the processes running in the computer, it is only acceptable to state that the faster the CPU is, the faster the applications can run. However, a very large CPU is also not necessary for most home computers, as many of us do not run that many programs at a single time.
There are two typical components of a CPU: arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and the control unit (CU). The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations, while the CU extracts instructions from memory and decodes and executes them; calling on the ALU for help when necessary.
 A microprocessor incorporates all of the functions of a computer’s CPU on a single integrated circuit (IC). Initially, it required more than one circuit in order to house the CPU, as the technology became more advanced, the need for that many circuits reduced. Today a microprocessor can house around 4 CPUs for quad-core technologies. In addition to the CPU, the microprocessor also packs I/O and memory access circuits. It is a programmable device that receives data, processes it according to stored directions and then gives results in the form of output. The primary language is binary code, a system of 1 and 0s.
A microprocessor incorporates all of the functions of a computer’s CPU on a single integrated circuit (IC). Initially, it required more than one circuit in order to house the CPU, as the technology became more advanced, the need for that many circuits reduced. Today a microprocessor can house around 4 CPUs for quad-core technologies. In addition to the CPU, the microprocessor also packs I/O and memory access circuits. It is a programmable device that receives data, processes it according to stored directions and then gives results in the form of output. The primary language is binary code, a system of 1 and 0s.
Microprocessors are responsible for controlling the logic of almost all digital devices. The internal working of a microprocessor depends on the design and purpose of the microprocessor. It is limited by number of transistors that can be placed on the chip, the number of package terminations that can connect the processor to the other parts of the computer, the number of interconnections possible and the amount of heat that the chip generates. In short, the microprocessor is a set of circuits that connect the rest of the computer to the CPU, allowing the system to execute directions. Many microprocessor also exist without CPUs attached to it.
Due to the similarity in usage, it is easy to understand why both of these words have become synonymous. If a person were to refer to a microprocessor as a CPU and vice-versa, it would be acceptable.
Image Courtesy: en.wikipedia.org, kids-online.net









Comments
arti rajawat chitawa
Tue, 08/09/2016 - 18:21
Leo Towett
Thu, 12/17/2015 - 12:38
Add new comment