Difference between Male and Female Circumcision
Key Difference: Male circumcision is the process of removing the foreskin that covers the head of the penis. Female Circumcision is the process of removing part or complete external female genitalia. It is also known as Female Genital Mutilation, or FGM.
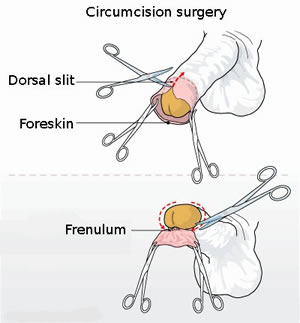 Circumcision is a widely debated topic that borders the line on ethics and religion. To many people, male and female circumcision are the same – mutilation of the private area of a child without their consent. However, there are also others that claim male and female circumcision are completely different from each other. In technicality, male and female circumcision differ from each other in many ways.
Circumcision is a widely debated topic that borders the line on ethics and religion. To many people, male and female circumcision are the same – mutilation of the private area of a child without their consent. However, there are also others that claim male and female circumcision are completely different from each other. In technicality, male and female circumcision differ from each other in many ways.
Male and female sexual organs develop during the end of the first trimester of pregnancy. The male sexual organs develops into a penis with a tissue based covering known as foreskin. The female sexual organs develops into a small penile-like extension, known as the clitoris. Over the clitoris, a foreskin like material develops that covers the clitoris – this is known as ‘hood’ or labia. Other developments includes a vaginal hole that is also covered by this hood.
Male circumcision is the process of removing the foreskin that covers the head of the penis. Although, originally circumcision only included removing the tip of the foreskin, which extended the end of the glands. This ensured that men would have easier erections and fertility would increase. As the years passed, it was decided that in addition to just the tip of the foreskin (known as partial circumcision), men would have the whole foreskin removed (also known as full circumcision).
Male Circumcision has been divided into four types:
Type I – Removal of all prepuce beyond the glands (This includes removal of the tip of the foreskin)
Type II – Removal of all prepuce (Removing the foreskin at the head of the penis)
Type III – Removal of all skin (including scrotum)
Type IV - Sub incision (Any cuts, pricks and incisions made to the penis)
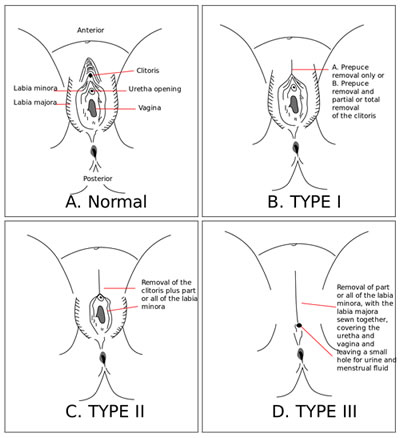 Female Circumcision is the process of removing part or complete external female genitalia. It is also known as Female Genital Mutilation, or FGM. The procedure includes using blades or razors with little to no anesthesia. The process differs depending on the area. In some areas, circumcision removes only a part of the clitoris or the full clitoris. While, in other areas a severe form of circumcision is performed – known as infibulation. Infibulation requires the removal of the clitoris, the clitoral hood, clitoral glands, the inner and the outer labia, and the closure of the labia. The rest is stitched up again with only a small hole left open for urination and menstrual cycle.
Female Circumcision is the process of removing part or complete external female genitalia. It is also known as Female Genital Mutilation, or FGM. The procedure includes using blades or razors with little to no anesthesia. The process differs depending on the area. In some areas, circumcision removes only a part of the clitoris or the full clitoris. While, in other areas a severe form of circumcision is performed – known as infibulation. Infibulation requires the removal of the clitoris, the clitoral hood, clitoral glands, the inner and the outer labia, and the closure of the labia. The rest is stitched up again with only a small hole left open for urination and menstrual cycle.
Female Circumcision is also divided into four types:
Type I – Partial or total removal of the clitoris and/or the prepuce
Type II – Partial or total removal of the clitoris and the labia minora, with or without excision of the labia majora
Type III – Narrowing of the vaginal orifice with creation of a covering seal by cutting and appositioning the labia minora and/or the labia majora, with or without excision of the clitoris
Type IV – All other harmful procedures to the female genitalia for non-medical purposes, for example: pricking, piercing, incising, scraping and cauterization.
Both circumcisions are viewed completely differently worldwide, with the male circumcision being legal and the FGM being illegal. The reasons for the circumcision also differ with the male one being as a manner of being closer to God. However, female circumcision is regarded as a form of purifying the woman and also to control her sexual desires.
Comparison between Male and Female Circumcision:
|
|
Male Circumcision |
Female Circumcision |
|
Development of Sexual Organs |
End of first trimester |
End of first trimester |
|
Age of Circumcision |
Usually childhood and in some rare cases, teenage |
Childhood as well as when child reaches puberty |
|
Types of Circumcision |
Type I – Removal of all prepuce beyond the glands Type II – Removal of all prepuce Type III – Removal of all skin (including scrotum) Type IV - Sub incision |
Type I – Partial or total removal of the clitoris and/or the prepuce Type II – Partial or total removal of the clitoris and the labia minora, with or without excision of the labia majora Type III – Narrowing of the vaginal orifice with creation of a covering seal by cutting and appositioning the labia minora and/or the labia majora, with or without excision of the clitoris Type IV – All other harmful procedures to the female genitalia for non-medical purposes, for example: pricking, piercing, incising, scraping and cauterization. |
|
What it removes |
Originally only the tip of the foreskin was removed. Now, most commonly the full foreskin on the tip of the penis is removed. |
There are a few types: removing only the clitoris, or the removal of clitoris and labia. It can also include complete removal of the folds, the labia and clitoris and the vagina is re-stitched leaving only a small hole for urination. |
|
Reason for circumcision |
Religious – to be closer to God. Also, cultural reasons are often cited. |
To control the girl’s sexual desire is the most common reason cited. Other reasons include religion and culture. |
|
Changes in sexual nature |
There are no changes in sexual behavior. Circumcision does not alter a man’s ability to have an orgasm |
Changes in sexual behavior. Circumcision alters a women’s ability to have an orgasm as well as perform sexually |
|
Infection |
Low risk for infections |
Increases risk for infections |
|
Pain |
Is comparatively less painful |
Is comparatively more painful |
|
Healing |
A few days to a week |
Months to sometimes a year |
|
Complications |
Has low risk for complications |
Has higher risk for complications |
|
Legality |
Is considered legal in many nations |
Is considered illegal in many nations |
Images Courtesy: en.wikipedia.org







Comments
Kess Westler #E...
Sun, 11/19/2017 - 18:18
Matthew
Fri, 09/08/2017 - 05:31
Anonymous
Wed, 03/21/2018 - 09:28
Anonymous
Sun, 10/01/2017 - 23:53
Add new comment