Difference between Casting and Forging
Key Difference: Forging and casting are two different techniques used for transforming metal materials into the desired form in context to shape and size. Forging makes use of compressive forces, whereas casting makes use of mold cavities where metal liquid is poured and then solidified to form into the desired shape. Forging process is considered to be better than casting due to its production of parts with denser microstructures, better grain patters and less porosity.
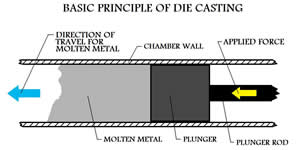 Forging and casting are two different techniques used in the manufacturing process. They both are different from each other. Casting generally makes used of the heating. This heat is supplied to the material. For casting, material must be heated above its melting temperature. The material liquefies and melts. This liquefied material is poured into a mold, where it takes its shape and then takes a desored solid state.
Forging and casting are two different techniques used in the manufacturing process. They both are different from each other. Casting generally makes used of the heating. This heat is supplied to the material. For casting, material must be heated above its melting temperature. The material liquefies and melts. This liquefied material is poured into a mold, where it takes its shape and then takes a desored solid state.
 On the other hand, forging makes use of the compressive forces for reshaping or deforming the material. It is used in order to apply a geometric change to the material. This process of forging is mainly used in the iron and steel manufacturing industry. Forgings are famous for making some of the strongest manufactured parts as compared to the parts made by employing other techniques.
On the other hand, forging makes use of the compressive forces for reshaping or deforming the material. It is used in order to apply a geometric change to the material. This process of forging is mainly used in the iron and steel manufacturing industry. Forgings are famous for making some of the strongest manufactured parts as compared to the parts made by employing other techniques.
It tends to strengthen the material by taking care of the cracks and waste spaces within the metal by sealing them. There are different types of forging processes like impression die forging, cold forging, open die forging and seamless rolled ring forging.
Therefore, casting and forging are different from each other. Forged parts have higher tensile sand fatigue strength than the casted parts. Both casting and forging have their own sets of advantages like casting provides a large range of alloy choices. The tools used in casting are cheaper than the ones employed in forgings. Casting has no problem in dealing with the complicated parts.
Forging is preferred for being tougher than other techniques. The tight grain structure acquired through forging provides super wear resistance. Forgings are also considered to be more reliable than casting as forging avoids the occurrence of metallurgical defects which can occur during the casting process. Casting provides the flexibility of producing the desired shape of any thickness. After producing a good casting prototype, one can use this prototype for the mass production.
Comparison between Casting and Forging:
|
|
Casting |
Forging |
|
Definition |
A manufacturing process in which molten metal material is poured into molds to create the desired shape |
A manufacturing process which makes use of compressing forces to enhance rigidity |
|
Tensile and Fatigue strength |
Lesser |
Higher |
|
State of the metal |
Involves pouring of molten metal into a mold for cooling |
Can be done to cold, warm and hot metal depending on the requirement of the final product. |
|
Metallurgical defects |
Can occur |
Avoided |
|
Response to heat treatment |
Requires close control due to the probability of alloy segregation |
Better |
|
Main materials used |
Original matter is in the state of ingot, metal powder or molten metal Casting process involves materials of metal, wood, fuel and mold |
Include carbon steel, alloy steel, bronze, steel, magnesium and other alloys |
|
Types |
Gravity casting (including sand casting and die casting) and pressure casting (including low pressure casting and high pressure casting). |
Impression die forging, cold forging, open die forging and seamless rolled ring forging. |
Image Courtesy: thelibraryofmanufacturing.com, greatergood.berkeley.edu








Comments
rakeshkrishnanr...
Fri, 02/09/2018 - 15:40
Ajay Kumar
Tue, 04/11/2017 - 18:32
Add new comment