Difference Between Cell and Tissue
Key difference: Cells are the smallest unit of life which form the basis of an organism. Tissues are groups of like minded cells working together.

Cells and tissues are both structurally imported in an organism. Without each the organism will not be able to function. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are microscopic in nature, which means that they can’t be seen with the naked eye. Tissues are groups of similar cells, working towards a single objective.
Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke and were named for the small “cells” (rooms) in a monastery. Cells are the smallest objects in the organism. All creatures came from one cell, a single fertilized egg, which then keeps splitting and developing until the organism is ready to enter the world. Humans each contain about 10 trillion cells.
In 1839, Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann developed the cell theory, which stated that that all organisms are composed of one or more cells. The theory surmised that all cells come from preexisting cells and that vital functions of an organism occur within cells. The theory also stated that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells.
There are two types of cells, the prokaryotic cells and the eukaryotic cells. The prokaryotic cells are self-sufficient in nature, such as bacteria
and archaea. On the other hand, the cells of all multi-cellular beings are eukaryotic cells. Cells typically contain organelles such as
mitochondria, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, ribosomes, nucleus, etc. Each of these organelles perform a different function in the cell. For example, a nucleus contains all the genetic information of the cell or animal and regulates all the activities inside a cell, whereas, mitochondria is responsible for performing the metabolic activities.
A group of cells that are like-minded i.e. perform the same function, come together to form tissues. The cells are not exactly identical, but have the same origin. Plasma
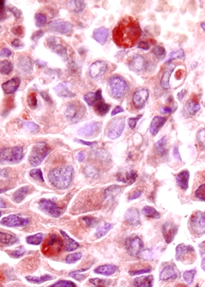
connects these cells together, to give tissue its form. A non-living matrix called the extra cellular matrix (ECM) interlinks and separates cells within a tissue. Like-minded tissues then group together to form organs. These organs then perform the important functions of the body.
Cells and tissues are very important in the body. Every function of the body is executed through cells. One can understand the importance, when one realizes that the even a slight alteration of a particular cell can result in an irreversible mutation or into cancer.
|
|
Cell |
Tissue |
|
Definition |
Cells are smallest unit of life. |
Group of like minded cells. |
|
Components |
Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, ribosomes, nucleus, etc. |
Similar cells |
|
Types |
Eukaryotic Cell And Prokaryotic Cell |
Epithelial tissue, nerve tissue, muscle tissue, and connective tissue. |
|
Developmental processes |
Mitosis or meiosis |
Tissue repair through regeneration and fibrosis |
|
Functions |
Growth, metabolism, creation, and protein synthesis. |
Group of similar cells come together to perform a similar function and to form organs. |
Image Courtesy: futurity.org, rndsystems.com








Comments
Ibrahim
Sun, 09/17/2017 - 17:50
Add new comment