Different types of Operating System
Key difference: Operating Systems, shortly OS is an intermediate between the computer hardware and users. It is a collection of software which manages the computer hardware resources and provides common services for computer programs. Today, there are different types of standard operating systems which are developed and used as middleware.
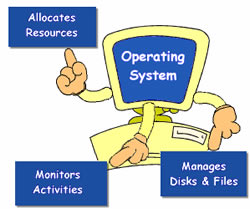 Operating systems (OS) are known to simplify and provide the human computer interactions. These are responsible for connecting the user-defined application programs with the hardware; due to which it becomes easy to access over the computers. They host several applications which run on computers and hence handle the operations related to their functioning with that of the computer. Hence, Operating Systems are essential component of computer system software; as all the application programs usually function and run on these operating systems.
Operating systems (OS) are known to simplify and provide the human computer interactions. These are responsible for connecting the user-defined application programs with the hardware; due to which it becomes easy to access over the computers. They host several applications which run on computers and hence handle the operations related to their functioning with that of the computer. Hence, Operating Systems are essential component of computer system software; as all the application programs usually function and run on these operating systems.
According to the developing Computer and Information technology, there has been a tremendous growth in the development sector. Today, there are different types of Operating system, which acts as a middleware between the hardware and the user, thereby providing easy and understanding interactions.
Comparison of various Operating Systems:
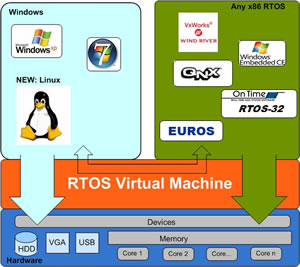
- Real-Time Operating System:
Real-time Operating System also known as RTOS; are used for managing the control machinery, scientific instruments and industrial systems. It manages the computer resources and handles the operation in a precise way by providing equal amount of time for every operation. It has very little user-interface capability, and no end-user utilities.
There are two types of real-time operating systems.
Hard Real-Time Systems- the system guarantee the completion of the critical task on time. In this system, the secondary storage is limited or missing with data stored in ROM and the virtual memory is also almost never found.
Soft Real-Time Systems- these are less restrictive and hence these give the first priority to the critical tasks than the other tasks. They retain the priority until the task gets completed. These have limited utility than hard real-time systems. For example, Multimedia, Virtual Reality, Advanced Scientific Projects like undersea exploration and planetary rovers etc.
 Single-User, Single Task Operating System:
Single-User, Single Task Operating System:
From the names itself it gets clear that these operating systems work on single task and single user at a time. Here, a single tasks or operation can be carried out efficiently and thoroughly by a single user. The Palm OS for Palm handheld computers is a good example of a modern single-user, single-task operating system.

- Single-User, Multi-Task Operating System:
These operating systems works on more than one task and process them concurrently at a time. The processors of this OS divides the time among the several executed tasks. This division of time is called as Time Sharing systems. Here, the processors switch rapidly between the processes. For example, the user can listen to music on the computer while writing an article using word processor software. Users can also switch between the applications and transfer the data between them; Windows 95 and all later versions of Windows are examples of multitasking OS.
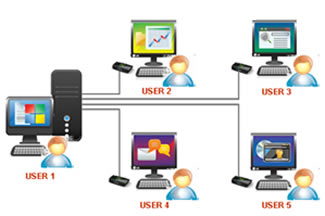
- Multiuser Operating System:
In these OS, multiple users are allowed to access the same data or information at a time via a network. The users can also interact among each-other. Some examples of this type of Os are: Linux, UNIX, and Windows 7.
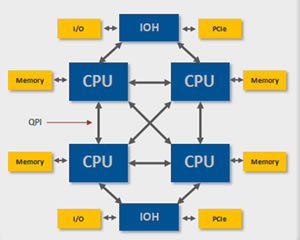
- Multiprocessing Operating System:
Here, a single process runs on two or more processors. All the processing and their management takes place in a parallel way, hence this OS are also called as Parallel Processing. Each processor works on different parts of the same task, or, on two or more different tasks. As their execution works in parallel, these are applicable for high speed execution, and also to increase the power of computer. For example: Linux, UNIX and Windows 7 are examples of multiprocessing OS.
.jpg) Embedded Operating System:
Embedded Operating System:
These are embedded in a device, which is located in ROM. These are applicable and developed only for the needed resources and accordingly developed. These OS are less resource intensive. Mainly, applicable in appliances like microwaves, washing machines, traffic control systems etc.
.jpg)
- Distributed Operating System:
In these OS, the computers work in co-operation with each other. As this OS manages a group of independent computers and makes them appear to be a single computer is known as a distributed operating system.
 Along with these OS, the other developed OS are Mobile Operating Systems, which are now famous in all types of latest and developed mobiles; among them the most renowned and famous are the Android OS with all multitasking and application features. In Batch Processing and Interactive Systems, the execution of programs takes place in batches. The Online and Offline Processing Systems offers the processing of data in online mode.
Along with these OS, the other developed OS are Mobile Operating Systems, which are now famous in all types of latest and developed mobiles; among them the most renowned and famous are the Android OS with all multitasking and application features. In Batch Processing and Interactive Systems, the execution of programs takes place in batches. The Online and Offline Processing Systems offers the processing of data in online mode.
Some of the most used Oerating systems in todays market are listed below:
Linux / Ubuntu, MacOS, MS-DOS, IBM OS/2 Warp, Unix / Variants, Windows CE, Windows 3.x, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, Windows ME, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7
Image Courtesy: jegsworks.com, citlindia.com, computinnovative.blogspot.com, cowputing.wordpress.com, benjenonline.com, ni.com, jijesoft.com, isocial-itn.eu, brandbuilderwebsites.com








Comments
educating
hamphery
Fri, 07/18/2014 - 16:43
Add new comment